biological_molecules_facts
... coiled forming a compact molecule. It is used for storage. Starch is tested with iodine solution, giving a blue-black colour change. Glycogen is a polysaccharide formed in animal cells. It is very branched. Cellulose is a polysaccharide formed from -glucose molecules. It has straight chains that ar ...
... coiled forming a compact molecule. It is used for storage. Starch is tested with iodine solution, giving a blue-black colour change. Glycogen is a polysaccharide formed in animal cells. It is very branched. Cellulose is a polysaccharide formed from -glucose molecules. It has straight chains that ar ...
practice exam
... E. a pH profile for an enzyme with two key ionized residues: a cysteine with pKa 4.2 and a Histidine with pKa 8.2 F. Saturation curve for myoglobin and hemoglobin (indicate which is which) ...
... E. a pH profile for an enzyme with two key ionized residues: a cysteine with pKa 4.2 and a Histidine with pKa 8.2 F. Saturation curve for myoglobin and hemoglobin (indicate which is which) ...
L12_FAS
... Or the PPP can be used to generate NADPH as an anti-oxidant – Particularly in red blood cells where a deficiency in G6PDH can cause anemia ...
... Or the PPP can be used to generate NADPH as an anti-oxidant – Particularly in red blood cells where a deficiency in G6PDH can cause anemia ...
Liver Function - Groby Bio Page
... What can excess carbon dioxide in the blood cause? Write down the chemical equation for formation of urea from ammonia? What is the scientific name for a liver cell. Name the 2 blood supplies to the liver What is the function of the Kupfer cell Name the enzyme that initially breaks down alcohol in t ...
... What can excess carbon dioxide in the blood cause? Write down the chemical equation for formation of urea from ammonia? What is the scientific name for a liver cell. Name the 2 blood supplies to the liver What is the function of the Kupfer cell Name the enzyme that initially breaks down alcohol in t ...
Lipid metabolism
... Use of ketone bodies by the extrahepatal tissues • acetoacetate and 3-hydroxybutyrate are reconverted to acetyl-CoA (→ citric acid cycle) • is located in matrix of mitochondria of the peripheral tissues • is significant in skeletal muscles, heart and also in the brain if lack of Glc occurs ...
... Use of ketone bodies by the extrahepatal tissues • acetoacetate and 3-hydroxybutyrate are reconverted to acetyl-CoA (→ citric acid cycle) • is located in matrix of mitochondria of the peripheral tissues • is significant in skeletal muscles, heart and also in the brain if lack of Glc occurs ...
Regulation of fatty acid synthesis and degradation by the AMP
... The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is the downstream component of a kinase cascade that is activated by rising AMP and falling ATP, which together signal a fall in cellular energy status. Although it probably has many targets, two key targets are acetylCoA carboxylase-1 and -2 (ACCI and ACCZ), ...
... The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is the downstream component of a kinase cascade that is activated by rising AMP and falling ATP, which together signal a fall in cellular energy status. Although it probably has many targets, two key targets are acetylCoA carboxylase-1 and -2 (ACCI and ACCZ), ...
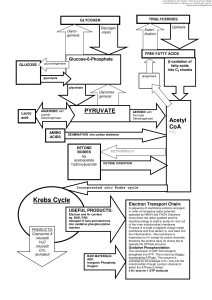
C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in Morrison 007
... the way to being made into fat. Write all the enzymes in the list below into the proper places in the figure below. If the enzyme is not used, write its name in the “not used” box. If it is used, write the enzyme in the order that the carbon atoms from glucose encounter the enzymes. ...
... the way to being made into fat. Write all the enzymes in the list below into the proper places in the figure below. If the enzyme is not used, write its name in the “not used” box. If it is used, write the enzyme in the order that the carbon atoms from glucose encounter the enzymes. ...
D2145 Systems Biology
... The TCA cycle is responsible for oxidizing pyruvate a. Explain where energy compounds are synthesised during the cycle (4 Marks) ...
... The TCA cycle is responsible for oxidizing pyruvate a. Explain where energy compounds are synthesised during the cycle (4 Marks) ...
1. The table shows the number of carbon atoms contained in some
... The table shows the number of carbon atoms contained in some substances. Substance ...
... The table shows the number of carbon atoms contained in some substances. Substance ...
High carbohydrate diet : which reduces gluconeogenesis by
... 1-Glucogenic amino acids: Amino acids which form glucose are pyruvate forming amino acids like alanine, glycine, serine, cysteine, cystine, and threonine. Those that produce intermediates of TCA cycle like oxaloacetic acid and - ketoglutarate. These amino acids come from degradation of muscle prot ...
... 1-Glucogenic amino acids: Amino acids which form glucose are pyruvate forming amino acids like alanine, glycine, serine, cysteine, cystine, and threonine. Those that produce intermediates of TCA cycle like oxaloacetic acid and - ketoglutarate. These amino acids come from degradation of muscle prot ...
Fuel Metabolism
... synthase (32). Hence, the energy that would normally be trapped in ATP is released as heat ...
... synthase (32). Hence, the energy that would normally be trapped in ATP is released as heat ...
All the following is correct about ribosomes EXCEPT
... Each nucleotide consists of three parts, these parts are a. a nitrogen base, a triose sugar and a phosphate group b. a nitrogen base, a hexose sugar and a phosphate group c. a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate group d. a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar and 2 phosphate group ...
... Each nucleotide consists of three parts, these parts are a. a nitrogen base, a triose sugar and a phosphate group b. a nitrogen base, a hexose sugar and a phosphate group c. a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate group d. a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar and 2 phosphate group ...
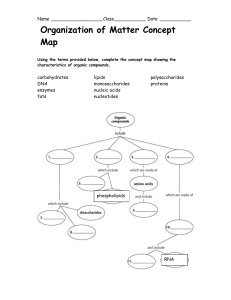
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... 8-18. Complete the chart below. Remember mono means one and poly means many. ...
... 8-18. Complete the chart below. Remember mono means one and poly means many. ...
BIO 330 Cell Biology Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Chapter 9
... AMP and Acetyl CoA regulate both pathways C. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis Phosphofructokinase (PFK) 2 is a bifunctional enzyme cAMP inhibits PFK 2 indirectly with regards to its kinase activity cAMP upregulates PKF 2 indirectly with regards to its phosphatas ...
... AMP and Acetyl CoA regulate both pathways C. Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis Phosphofructokinase (PFK) 2 is a bifunctional enzyme cAMP inhibits PFK 2 indirectly with regards to its kinase activity cAMP upregulates PKF 2 indirectly with regards to its phosphatas ...
Respiration and Lipid Metabolism Aerobic
... Outside membrane Oxidize NADH & NADPH Inside membrane Oxidize NADH & NADPH Rotenone resistant pathway for NADH oxidation ...
... Outside membrane Oxidize NADH & NADPH Inside membrane Oxidize NADH & NADPH Rotenone resistant pathway for NADH oxidation ...
Tymoczko, Biochemistry: A Short Course 3e, Launchpad
... a. products of reactions between reducing sugars and free amino groups. b. two or more sugars joined together in a covalent bond. c. products of a reaction between sucrose and proteins. d. solely composed of long carbohydrate polymers on free amino groups. 7. Human blood groups (ABO) are a. the resu ...
... a. products of reactions between reducing sugars and free amino groups. b. two or more sugars joined together in a covalent bond. c. products of a reaction between sucrose and proteins. d. solely composed of long carbohydrate polymers on free amino groups. 7. Human blood groups (ABO) are a. the resu ...
some of Chapter 25
... Lipid synthesis acetyl-CoA many DHAP glycerol some lipids are essential we can’t make them we have to ingest them linoleic acid, linolenic acid ...
... Lipid synthesis acetyl-CoA many DHAP glycerol some lipids are essential we can’t make them we have to ingest them linoleic acid, linolenic acid ...
BioN08 Metabolism of lipids Summer 2015
... • Instead, they are absorbed into the lymphatic system through lacteals within the villi and are carried to the thoracic duct where the lymphatic system empties into the bloodstream. • These are the lowest-density lipoproteins because they carry the highest ratio of lipids to proteins. ...
... • Instead, they are absorbed into the lymphatic system through lacteals within the villi and are carried to the thoracic duct where the lymphatic system empties into the bloodstream. • These are the lowest-density lipoproteins because they carry the highest ratio of lipids to proteins. ...
Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ketone Bodies
... bodies in urine. Ketosis: the overall condition is called ketosis. ...
... bodies in urine. Ketosis: the overall condition is called ketosis. ...
Exam I will be on lectures 1 to 6 (Introduction to )
... c. carbon atoms joined by single bonds. d. carbon atoms joined by double bonds. e. oxygen atoms joined by double bonds. ...
... c. carbon atoms joined by single bonds. d. carbon atoms joined by double bonds. e. oxygen atoms joined by double bonds. ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... Enzymes act on specific substrates ◦ Substrate: substance that the enzyme breaks down Each substrate fits into the active site. (Like a lock & key) ...
... Enzymes act on specific substrates ◦ Substrate: substance that the enzyme breaks down Each substrate fits into the active site. (Like a lock & key) ...
Lipid Metabolism
... • Esters of fatty acids with glycerol; mono-di- or triacylglycerol (TAG). • The main storage form of fuel in animals is TAG. • It is stored in adipose tissues. • It is hydrophobic molecule, therefore it is transported in blood by the lipoprotein particles mainly chylomicrons and very low density lip ...
... • Esters of fatty acids with glycerol; mono-di- or triacylglycerol (TAG). • The main storage form of fuel in animals is TAG. • It is stored in adipose tissues. • It is hydrophobic molecule, therefore it is transported in blood by the lipoprotein particles mainly chylomicrons and very low density lip ...
Sample exam 1
... b. At these physiological conditions, ATP hydrolysis has a free energy change of – 58 kJ/mol. How many moles of ATP must be hydrolyzed to generate the gastric juice in part a? 8. Even though acetate units, such as those obtained from fatty acid oxidation, cannot be used for net synthesis of carbohyd ...
... b. At these physiological conditions, ATP hydrolysis has a free energy change of – 58 kJ/mol. How many moles of ATP must be hydrolyzed to generate the gastric juice in part a? 8. Even though acetate units, such as those obtained from fatty acid oxidation, cannot be used for net synthesis of carbohyd ...
Glyceroneogenesis

Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate or triglyceride from precursors other than glucose. Usually glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, but when glucose concentration drops in the cytosol, it is generated by another pathway called glyceroneogenesis. Glyceroneogenesis uses pyruvate, alanine, glutamine or any substances from the TCA cycle as precursors for glycerol 3-phophate. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which is an enzyme that catalyses the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate is the main regulator for this pathway. Glyceroneogenesis can be observed in adipose tissue and also liver. It is a significant biochemical pathway which regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorder such as type 2 diabetes.