* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. The table shows the number of carbon atoms contained in some
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
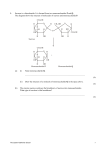
1. The table shows the number of carbon atoms contained in some substances. Substance Number of carbon atoms Amino acid 2 - 11 Glycerol Glucose 6 Pyruvate Starch (a) Large and variable number Complete the table to show the number of carbon atoms in glycerol and pyruvate. (2) (b) Explain why the number of carbon atoms (i) may vary from 2 to 11 in an amino acid molecule; ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) may be described as variable in a starch molecule. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Explain why the type of chemical reaction in which glucose is converted to starch may be described as condensation. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) The Queen Katherine School 1 2. The diagrams show five molecules A to E. B A CH 2 OH R H2N C H COOH O H OH H OH H H OH H OH D C H H C OH H C OH H C OH H E Which molecule, A to E, (a) is one of the monomers which combine to form starch; .................... (b) contains peptide bonds: .................... (c) could be an oil; .................... (d) is one of the molecules that form a triglyceride? ................... (4) (Total 4 marks) The Queen Katherine School 2 3. The diagrams show four types of linkage, A to D, which occur in biological molecules. Amino acid H C H S S A Amino acid H O H C C N B H O H H O C (a) H H C O O C R D Name the chemical process involved in the formation of linkage B. ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Give the letter of the linkage which (i) occurs in a triglyceride molecule; ......................................................................................................................…. (1) (ii) might be broken down by the enzyme amylase; ......................................................................................................................…. (1) (iii) may occur in the tertiary, but not the primary structure of protein. ......................................................................................................................…. (1) (c) Describe how a saturated fatty acid differs in molecular structure from an unsaturated fatty acid. ................................................................................................................................…. ..................................................................................................................................… ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) The Queen Katherine School 3