* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Sucrose is a disaccharide. It is formed from two
Survey
Document related concepts
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
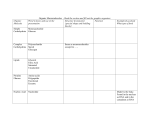
1. Sucrose is a disaccharide. It is formed from two monosaccharides P and Q. The diagram shows the structure of molecules of sucrose and monosaccharide P. CH 2 OH O H H OH H O OH H O CH 2 OH H OH H H HO CH 2 OH OH H Sucrose CH 2 OH O H H OH H OH Monosaccharide P (i) + H OH (a) H OH Monosaccharide Q Name monosaccharide Q. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Draw the structure of a molecule of monosaccharide Q in the space above. (1) (b) The enzyme sucrase catalyses the breakdown of sucrose into monosaccharides. What type of reaction is this breakdown? ..................................................................................................................................... (1) The Queen Katherine School 1 (c) The diagram shows apparatus used in breaking down sucrose. The enzyme sucrase is fixed to inert beads. Sucrose solution is then passed through the column. Sucrose solution Sucrase fixed to beads Gauze Products Describe a biochemical test to find out if the solution collected from the apparatus contains (i) the products; ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) the enzyme. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) The Queen Katherine School 2 2. The table shows the number of carbon atoms contained in some substances. Substance Number of carbon atoms Amino acid 2 - 11 Glycerol Glucose 6 Pyruvate Starch (a) Large and variable number Complete the table to show the number of carbon atoms in glycerol and pyruvate. (2) (b) Explain why the number of carbon atoms (i) may vary from 2 to 11 in an amino acid molecule; ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) may be described as variable in a starch molecule. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (c) Explain why the type of chemical reaction in which glucose is converted to starch may be described as condensation. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) The Queen Katherine School 3