* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
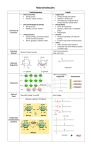
Biology 12 Ms. Kuiper Name: Block: Biology 12 – Biological Molecules – Review Worksheet Part A: Mix and Match: Match the term on the right with the definition on the left. Each term can be used only once. Write the letter of the best answer in the box to the left of the definition. (1/4 mark each -- total of 10 marks for this section) Q P DD I W C J GG 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) BB 9) B 10) Y II 11) 12) H 13) O 14) K A E Z 15) 16) 17) 18) T R N 19) 20) 21) F M HH X G 22) 23) 24) 25) 26) V CC AA EE FF JJ U S D L LL KK 27) 28) 29) 30) 31) 32) 33) 34) 35) 36) 37) 38) water-"loving" water-"fearing" two or more polypeptide chains coming together and bonding with each other to permanently change the 3 dimensional structure of a protein the subunit that makes up nucleic acids - 4 types in DNA are A C G T the smallest unit of matter that cannot normally be broken into smaller particles the process of breaking down large fat droplets into smaller fat droplets the loose association of amino acids in a polypeptide chain with each other, usually through H-bonds. e.g. alpha helix, beta pleated sheet the linear sequence of amino acids in a protein, which ultimately determines its shape the building block of protein -- there are 20 different kinds normally found in nature the bond that forms between two amino acids joined by dehydration synthesis the 3-D shape of a polypeptide chain due to it folding back on itself and forming bonds. creating a bond between two atoms by taking OH from one atom and H from the other breaking a bond between two atoms by adding OH to one atom and H to the other biological catalysts, composed of protein, that speed up chemical reactions ATP - the molecule that carries energy in the cell any molecule with the molecular formula Cn(H2O)n an important component of cell membranes, has a hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tail an enzyme that breaks down maltose to two glucose molecules an atom or molecule that has either lost or gained electrons a weak bond due to the attraction between partial charges on hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms a polymer of glucose, used as a structural component of plant cell walls a polymer of glucose, used as a storage form for glucose in animals a polymer of glucose, used as a storage form for glucose in plants a loss of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a lipid that is an important component of cell membranes and from which steroid hormones are made a lipid composed of glycerol joined to 3 fatty acids a large organic molecule formed from a chain or chains of amino acids a large molecule made by joining together smaller identical (or similar) molecules a gain of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a fatty acid whose carbons are all joined to the maximum number of hydrogens a fatty acid that has a "kink" in it due to a double bond between carbon atoms a disaccharide consisting of two glucose molecules a class of molecules that includes neutral fats and steroids a chemical that resists changes in pH a 6 carbon sugar that forms a 6-membered ring -- used as energy source by cells three carbon that joins with fatty acids to produce triglycerides molecules that store genetic information (e.g. DNA and RNA) A) B) C) D) E) F) G) H) adenosine triphosphate amino acid atom buffer carbohydrate cellulose cholesterol dehydration synthesis I) denature J) emulsification K) L) enzymes glucose M) glycogen N) hydrogen bond O) P) Q) R) hydrolysis hydrophobic hydrophilic ion S) T) U) lipid maltase maltose V) W) X) Y) Z) neutral fat nucleotide oxidation peptide bond phospholipid AA) BB) CC) DD) EE) FF) GG) HH) II) JJ) KK) LL) polymer primary structure protein quarternary structure reduction saturated fatty acid secondary structure starch tertiary structure unsaturated fatty acid nucleic acids glycerol MOLECULE HANDOUT In order from left to right Water glucose maltose Animo acid dipeptide phospholipid Unsaturated fat saturated fat neutral fat (triglyceride) Cholesterol pyrimidine purine ATP DNA negative feedback loop