* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter-4 part-2 Energy Metabolism
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
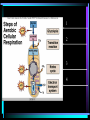
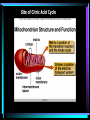
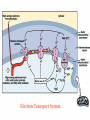
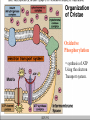
Chapter 4 Enzymes and metabolism part II Outline • Names of enzymes & types of reactions • ATP Production • Synthetic Pathways Enzymes • Normally end in “ase” • Normally are proteins • “Isozymes” may look different but catalyze the same reaction General types of reactions • Oxidation-reduction • Add or subtract e- or H+ • Hydrolysis-dehydration • Add H20 • Remove H20 • Transfer of groups • Exchange, add, or remove • Ligation • Link together Some examples of reactions Steps of ATP production 1 2 3 4 Glycolysis GLUCOSE PYRUVATE Site of Citric Acid Cycle Citric Acid Cycle or Krebs Cycle Electron Transport System Oxidative Phosphorylation = synthesis of ATP Using the electron Transport system. Chemiosmosis • Proteins of mitochondria have 2 purposes, to – Transport electrons – Transport hydrogen atoms Summary: Energy Yield from cellular respiration Final hydrogen acceptor is oxygen!! When ATP is broken down this reaction releases free energy. • Is this reaction exergonic or endergonic. • How would you measure free energy? • ATP can then yield 7-12 kcal/mole ATP What happens to ATP production without O2? What do we call metabolism without oxygen? Anaerobic Metabolism aerobic to 30-32 ATPs DECREASES anaerobic No O2! 2 ATPs Anaerobic Fermentation! Lactic acid fermentation Alcohol fermentation BIG BIOMOLECULES CAN BE BROKEN DOWN AND USED FOR ATP SYNTHESIS • Glycogenolysis • Lipolysis • Deamination BIG BIO Glycogenolysis: Energy from stored carbohydrates • Glycogen to glucose • Energy 4 kcal/gm Lipolysis: Energy from fat • Beta-oxidation • 9 kcal/gm fat • Excess Beta-oxidation can lead to “ketone bodies” Energy from proteins: Typically surplus proteins but sometimes not from surplus Aneroxia Nervosa Synthetic pathways • Glycerol or amino acids* • Glucose to • Glucose to to Glucose * gluconeogenesis Glycogen *glycogenesis Glycerol Triglycerides • Acetyl CoA to Fatty acids Glycogenesis Synthesis of glycerol and fatty acids The End