* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis of doxorubicin wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
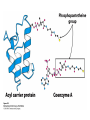
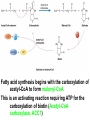
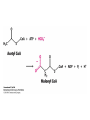
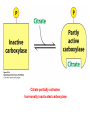
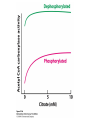
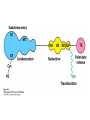
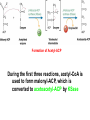
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Can occur in the cytoplasm of most animal cells, but the liver is the major site for this process Fatty acids are synthesized when the diet is low in fat or high in carbohydrate or protein (most from glucose via pyruvate) A large quantity of NADPH is needed for this process and is provided by the pentose phosphate pathway and oxidation of malate to form pyruvate by malic enzyme Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Similar to b-oxidation in reverse Several notable differences: 1. Location occurs in cytoplasm instead of mitochondria and peroxisome 2. Enzymes significantly different than in boxidation Comparison of the Phosphopantetheine Group in Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP) and in Coenzyme A (CoASH) 3. Thioester linkage - intermediates are linked through a thioester linkage to acyl carrier protein (ACP) Acyl groups linked to ACP through phosphopantetheine prosthetic group 4. Electron carriers consume NADPH Fatty acid synthesis begins with the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to form malonyl-CoA This is an activating reaction requiring ATP for the carboxylation of biotin (Acetyl-CoA carboxylase, ACC1) Regulation of Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase 1 ACC enzymes are highly regulated by allosteric modulators and phosphorylation Glucagon and AMPK lead to phosphorylation of ACC which inactivates the enzyme Insulin activates phosphoprotein phosphatase 2A which activates ACC glucagon insulin Citrate partially activates hormonally inactivated carboxylase The remaining reactions of fatty acid synthesis take place on fatty acid synthetase multienzyme complex Site of seven enzyme activities Fatty Acid Synthase Structure Two fatty acids constructed simultaneously Formation of Acetyl-ACP During the first three reactions, acetyl-CoA is used to form malonyl-ACP, which is converted to acetoacetyl-ACP by KSase During the next three steps (two reductions and a dehydration), a butyryl group is formed Butyryl is then transferred to KSase and the ACP-SH group can bind another malonyl group Eventually synthesizes palmitoyl-ACP Fatty Acid Biosynthesis