* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Cell - KerrBrookfield
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
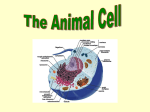
THE CELL May 22, 2017 1 Animal Cell Structure Animal Cell 1. no cell wall 2. no chloroplasts 3. no central vacuole 4. has centrioles flagella centrioles lysosome chromosomes nuclear pore nucleolus nuclear membrane cytoskeleton vacuole exocytosis RER (ribosomes) cell membrane golgi apparatus SER cytoplasm mitochondria May 22, 2017 2 Plant Cell Structure Plant Cell 1. cell wall 2. chloroplasts 3. a large central vacuole 4. no centrioles nuclear nuclear pore membrane nucleolus chromosomes RER (ribosomes) vacuole chloroplast cell wall cell membrane SER golgi apparatus cytoplasm mitochondria May 22, 2017 cytoskeleton 3 Structures of a Cell How many do you remember? Close all books and notes : ) cell wall ribosomes cilia / flagellum nuclear membrane large vacuole cell membrane cytoskeleton cytoplasm small vacuole centrioles secretory vesicles nucleolus mitochondria lysosome Golgi apparatus chloroplast nuclear pores rough endoplasmic reticulum May 22, 2017 nucleoplasm (chromosomes) smooth endoplasmic reticulum 4 ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL Switch with a partner! Place a small checkmark next to the correct answers. Put their score out of 20 in the right hand corner. 1. nucleolus 2. nucleoplasm (chromosomes) 3. nuclear pores 4. nuclear membrane 5. small vacuole 6. secretory vesicles 7. Golgi apparatus 8. mitochondria 9. smooth endoplasmic reticulum 10. rough endoplasmic reticulum 11. ribosomes 12. cytoskeleton 13. cell membrane 14. cell wall 15. centrioles 16. large vacuole 17. lysosome 18. chloroplast 19. cilia / flagellum 20. cytoplasm VIDEO May 22, 2017 7 Plasma Membrane Also called the cell membrane The plasma membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell. May 22, 2017 8 Fluid Mosaic Model of Cell Membrane protein channel tunnels that allow water or specific small ions in/out of cell May 22, 2017 9 PLASMA MEMBRANE carbohydrate globular protein phospholipid fatty acid tails (hydrophobic) phosphate head (hydrophilic) protein channel Fluid Mosaic Model Plasma Membrane - Proteins May 22, 2017 11 Cytoskeleton mitochondrion microtubules microfilaments Functions of microfilaments and microtubules: 1. support the cell 2. make up centrioles 3. make up cilia & flagella General Structure of a Cell Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life. Cells are bathed in an aqueous solution called extracellular fluid. There are many different kinds of cells, which are specialized to carry out particular functions. In spite of this, cells have many common features. May 22, 2017 13 TEXTBOOKS • Please go take a textbook and return to your seat. (stretch while you are standing) • Start by reading Page 8… The Transmission Electron Microscope The Scanning Electron Microscope Make Jot Notes on those two sections. (3 points about each) Page # 9 complete # 4, 5 May 22, 2017 14 General Structure of a Cell Cell Part cell membrane cell wall cytoplasm ribosomes Plant, animal or both both plant Function •semi-permeable •controls what enters/leaves •composed of phospholipid bilayer, proteins, carbohydrates (fluid mosaic model) •tough rigid outer boundary •protection both •Cytosol (aqueous solution) and cell organelles outside the nucleus . both •make proteins General Structure of a Cell Cell Part smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Golgi apparatus lysosomes Plant, animal or both both Function •canals throughout cytoplasm to transport materials •make fats both •canals with ribosomes attached (area for protein synthesis) both •stacks of membranes which modify protein for secretion (export) •packages them into vesicles animal •contain enzymes (proteins) that can break down molecules (food, bacteria, wastes, the cell itself) General Structure of a Cell Cell Part Plant, animal or both Mitochondria both (write at the bottom) centrioles plastids vacuoles Function •powerhouse of the cell •produces energy (cellular respiration) animal •a pair of cylinders that aid in cell division plant •free-floating membrane-bound sac for storage example:chloroplast photosynthesis both •large (plants), small (animals) membrane-bound sacs filled with water •Turgor pressure General Structure of a Cell Cell Part nucleus nuclear membrane nucleoplasm nucleolus Plant, animal or both both both both both Function •control centre of the cell •directs all of the cell’s activities •porous double membrane •separates nucleus from cytoplasm •A mixture of chemicals that stores information •rich in nucleic acids •dense body in the centre of the nucleus thought to make ribosomes General Structure of a Cell Cell Part DNA Plant, animal or both Both CHLOROPLAST Do on your own! Function •genetic material •contains instruction for what proteins to make DNA occurs in two forms: 1. chromatin – long & thin (when cell is not dividing) 2. chromosomes – short & thick (during cell division) PRE-LAB: OBSERVING CELLS Recall: Microscope usage Proper Biological Diagrams Preparing Slides Your Task: Prepare a slide and draw a proper biological diagram of each of the following cells. TOTAL 4 DIAGRAMS Type of Cell Stain Used cheek cell methylene blue potato cell iodine tomato cell no stain red onion cell no stain PROPER BIOLOGICAL DIAGRAMS Name Type of Cell (stain used) Date Note: •Use blank white paper •Use pencil label 1 label 2 label 3 •Use a ruler •No colouring •No shading •No arrows •Labels must line up vertically •Label lines are parallel Total Magnification i.e. 400 X (Label lines do NOT cross) LAB: OBSERVING CELLS Your Task: Write a Formal Lab Report. Note: Discussion questions (1 – 3) are as follows. 1. What cell organelles were stained by methylene blue in cheek cells? 2. What cell organelles were you unable to find? Suggest two possible reasons for this. 3. Summarize in chart form the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells based on what you examined in this lab. Include differences in cell sizes in your answer. FORMAL LAB REPORT All formal lab reports must include the following: Title Page centred on the page Title of the Lab SBI 3C Your Name in the bottom right-hand corner Partner’s Name Ms. Kerr Date FORMAL LAB REPORT All formal lab reports must include the following: Purpose: One sentence stating the reason for doing the lab. Materials: A list of what you used during the lab. Procedure: A set of numbered steps. (Instructions) Observations: Biological diagrams and/or a chart with written observations. Discussion Questions: Answer all discussion questions using complete sentences. Conclusion: Briefly comment on the results of the lab (Make sure it relates to the purpose specifically.) Lab # 1 Observing Cells DUE : February 9, 2010 May 22, 2017 25 General Structure of a Cell Homework • Page 15 # 2, 3, 4, 5 ( we can do these together) Finish work from Tuesday: The microscope lab – hand in up until Friday Page 8 jot notes SEM and TEM Page 9 # 4 & 5