* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of the Cell
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
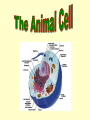
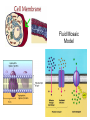
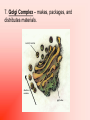
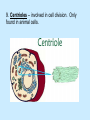
Aim: What are the structures and function of the animal and plant cells? I. Cell – the basic unit of structure and function in all living things. A. Animal Cell Structures 1. Cell (Plasma) Membrane a. Separates the cell from its environment b. Determines what enters and leaves the cell (selectively permeable). Fluid Mosaic Model 2. Cytoplasm – liquid gel that fills the cell. Site of all chemical activities and keeps the organelles from drying out. 3. Nucleus – “brain” of the cell. Contains the genetic (DNA,RNA) material that instructs the cell what to do. 4. Ribosome – site of protein synthesis. Found along the Endoplasmic Reticulum and floating freely in cytoplasm. 5. Mitochondria (mitochondrion – singular) – site of aerobic respiration (Energy production). 6. Endoplasmic Reticulum – transport for certain molecules to go to specific places. 7. Golgi Complex – makes, packages, and distributes materials. 8. Lysosome - This organelle digests waste materials and food within the cell. “Suicide sac.” 9. Centrioles – involved in cell division. Only found in animal cells. 10. Vacuole – Involved in storing foods and wastes to later be released. Animal cell vacuoles are smaller than plant cell vacuoles. A. Unique Plant Structures 1. Cell Wall – made of cellulose. Non-living. Gives plant cell its rectangular shape. 2. Large vacuole – stores food and wastes. 3. Chloroplasts – site of photosynthesis. Contains the molecule chlorophyll which gives plants its green color.