* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell reproduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
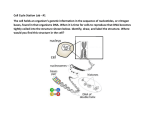
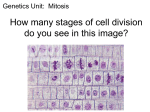
Cell Reproduction Prokaryotes Bacteria Eukaryotes Plants & animals Warm Up Mitosis Day #1 1. What process do prokaryotes use for cell division? 2. What are the two cells produced called? 3. Cells spend the most time in which stage of the cell cycle? 4. What happens during the S phase of the cell cycle? 5. What is another name for mitosis? Prokaryotes Lack a nucleus Have a single chromosome Reproduce by binary fission Include bacteria Steps in Binary Fission Used by bacteria Cells increase their cell mass slightly DNA & cell components are replicated Each cell divides into 2 daughter cells Binary Fission of Bacterial Cell E. Coli Dividing by Binary Fission Eukaryotes Contain a nucleus & membrane bound organelles Asexually reproduce cells by mitosis Cell Cycle Stages in growth & division G1 Phase S Phase G2 Phase M Phase Cytokinesis G1 Phase First growth stage Cell increases in size Cell prepares to copy its DNA and organelles increase in number Cells spend most of their time in this phase. Synthesis Phase (S) Copying of all of DNA’s instructions Chromosomes duplicated By the end of S stage the cell nucleus contains two complete sets of DNA G2 Phase Time between DNA synthesis & mitosis Cell continues growing Needed proteins produced M Phase ( Mitosis) Cell growth & protein production stop Cell’s energy used to make 2 daughter cells Called mitosis or karyokinesis (nuclear division) Life Cycle of a Cell Mitosis is a cycle with no beginning or end. Interphase – Resting Stage Cells carrying on normal activities while preparing for division By end of interphase cell has two full sets of DNA or chromosomes Cell is large enough to divide Occurs before mitosis Interphase Stages of Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cells Undergoing Mitosis Steps in Prophase DNA coils tightly & becomes visible as chromosomes Nuclear membrane disappears Nucleolus disappears Centrioles migrate to opposite poles Spindle fibers (microtubules) begins to form from centrioles and move toward center of cell Eukaryotic Chromosome Chromosome structure DNA wraps around proteins called histones forming chromatin. As cell progresses into mitosis, chromatin further condenses to form small thick rods. One half of a duplicated chromosome is called a chromatid. Together they are called a sister chromatid. Sister chromatids are held together by a centromere. Human Chromosomes Steps in Metaphase Spindle fibers from centrioles attach to each chromosome at the centromere. Cell preparing to separate its chromosomes Cell aligns its chromosomes in the middle of the cell Metaphase Steps in Anaphase Cell chromosomes (sister chromatids) are separated Spindle fibers shorten so chromosomes pulled to ends of cell Anaphase Steps in Telophase Separation of chromosomes completed Cell Plate forms (plants) Cleavage furrow forms(animals) Nucleus & nucleolus reform Chromosomes uncoil and spindle fibers fall apart Telophase Plant Animal Cytokinesis Occurs after chromosomes separate Forms two, identical daughter cells Cells will enter interphase and begin the cycle again. Cytokinesis Cell Plate formed by the golgi apparatus can’t pinch like animal cells because of cell wall.