* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 22 Cell Reproduction
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
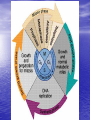
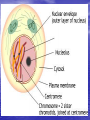
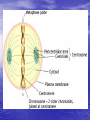
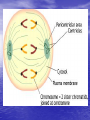
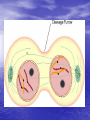
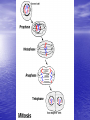
Do now!! What two (2) reasons do you think cells divide? Ch. 10 Cell Growth and Reproduction Why do cells divide? Body Growth and Repair • All living things grow • All living things need to repair themselves when injured • New cells are made to make these two things happen • The process of making new cells is called MITOSIS Cell Cycle • The life of a cell is called the cell cycle • It has five main phases – G1: this phase is for GROWTH and making new organelles. – S phase: this phase for SYNTHESIZING chromosomes. – G2: this phase is a second GROWTH phase dedicated to growing in size to prepare for cell division. – Mitosis: process of cell division – Cytokinesis: the end process of one cell becoming two cells Mitosis • Done in all the body cells of living things • Makes a copy of original cell • Done in four steps –Prophase –Metaphase –Anaphase –Telophase Prophase 1. Sister chromatids begin to shorten 2. 3. 4. and thicken into chromosomes Nuclear membrane begins to break down Centrioles move to the poles of the cell Spindle fibers form from each Centriole towards the center of the cell Metaphase 1. Centrioles are at opposite side of the cell 2. Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell 3. Spindle fibers attach to the centromere of the chromosome Anaphase 1. Chromosomes are pulled apart 2. Spindle fibers disintegrate after chromosome passes 3. Chromosomes are pulled towards the centrioles Telophase 1. Each side of the cell has a complete set of chromosomes 2. The cell starts to pinch in to split 3. Nucleus starts to reappear 4. CYTOKINESIS • At the very end of mitosis cytokinesis occurs • “Cyto”- meaning cell • -”kinesis” process of making new Correctly identify the following phases of the cell cycle. • Each number on the following picture represents a phase of the cell cycle • in you do now for the week place the correct name of the phase for each number. 2 1 3 4