* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure and function of cell components
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
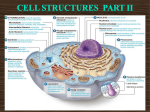
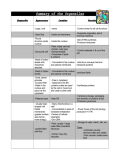
Structure and function of cell components (i) Carbohydrates (ii) Lipids (iii) Proteins (iv) Nucleic Acids (v) Membranes (vi) Cytoskeleton Structure of cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton is found in all eukaryote cells It is anchored in the cell membrane via membrane proteins It is composed of 3 types of fibre microfilaments Microtubules Found in all eukaryote cells Hollow tubes made of the protein tubulin Radiate from the MTOC (microtubule organising centre), stretch to plasma membrane MTOC changes length of microtubule by assembling and disassembly ends Microtubules can be assembled and disassembled rapidly Components of microtubules become spindle fibres during cell division Microtubules cont…. Function Provide structural support by resisting compression Have a role in organelle movement Separate chromatids during cell division Components of cilia, flagella and centrioles Microfilaments Made of actin protein Present throughout the cell, but most common just inside the plasma membrane Readily assembled and disassembled Function Involved in cell membrane movements e.g. Endocytosis / Phagocytosis Give cell shape Are part of the contractile ring that forms the two daughter cells during cytokinesis of animal cells Intermediate filaments Mostly made of keratin proteins Not found in all cells Probably permanent (cannot be assembled and disassembled) although cells may be able to regulate length Function Very stable tough fibres providing cell support Abundant in areas of a cell subject to mechanical stress Learning Activities Read and take notes from DART pg (5860) Scholar 5.3 Look back at the role of MTOCs and spindle fibres in cell division (cell cycle notes) Create a list of cytoskeleton functions and remember it Advanced Higher Questions