* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
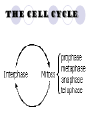
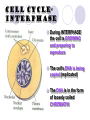
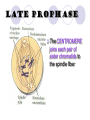
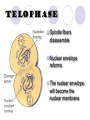
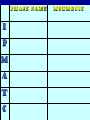
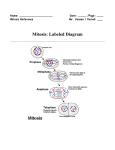
It’s The circle of cell life How do cells reproduce and grow? Why do cells divide? To replace other cells that have been damaged or worn out To allow multicellular organisms to grow For asexual reproduction Because they get too big! What is MITOSIS? Mitosis is the process by which the nucleus of one cell DIVIDES into two nuclei Therefore, each cell has the same genetic material as the original cell Its like “photocopying” the cell- the two daughter cells are identical Genetic Information Genetic information is contained in the DNA of the cell DNA is found in the thread-like coils called CHROMATIN when the cell is NOT dividing When the cell is dividing, the chromatin condenses (packs into) chromosomes genes are small sections of chromosomes that contain the information for a specific cell function The big picture Human Chromosomes The cell cycle Cell Cycle The cell spends the most amount of time in interphasegrowing Cell CycleInterphase During INTERPHASE the cell is GROWING and preparing to reproduce The cell’s DNA is being copied (replicated) The DNA is in the form of loosely coiled CHROMATIN Cell CycleMitosis Remember! Mitosis is the stages of the cell cycle in which the nucleus and cell divides Mitosis is divided into: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokenesis Cell Cycle The cell spends a very short amount of time in mitosisdividing The phases of mitosis Early Prophase Chromosomes are condensed and consist of 2 sister chromatids The nuclear membrane begins to break down Spindle fibers appear Late Prophase The CENTROMERE joins each pair of sister chromatids to the spindle fiber Metaphase Chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell Anaphase Spindle fibers separate sister chromatids and pull them apart Once they have separated they are individual chromosomes Telophase Spindle fibers disassemble Nuclear envelope reforms The nuclear envelope will become the nuclear membrane Cytokinesis In animal cells, cell membrane pinches off forming two new separate cells In plant cells, cell membrane pinches off and a cell wall forms The cytoplasm is divided between the two cells Mitosis in action! How am I going to remember this? Think IPMATC! Phase name I P M A T C mnemonic