* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
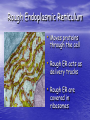
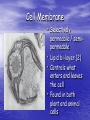
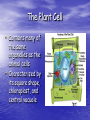
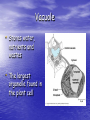
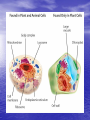
The Cell Structures and Functions The Eukaryotic Cell • Protists, Fungi, Plants and Animals are examples of Eukaryotes. • Although they are different, each of them contain many of the same cellular components Cellular Organelles • Organelle literally means “tiny organs” • Eukaryotic Cells contain cellular organelles that perform specific functions for the cell The Animal Cell • All animals including humans contain animal cells • These cells are individually specialized for specific functions Cytoplasm • A jelly-like substance that contains or holds of cell’s organelles The Nucleus • The brain of the cell • Contains all of an organisms genetic information • Controls ALL cellular functions The Nucleus Cont…… • Nucleolus- the center of the nucleus contains chromosomes and makes ribosomes • Nuclear Envelopeseparates nucleus from the cytoplasm The Mitochondrion • Supplies the energy needed by the cell • Also known as the “power house” of the cell • ATP is the cells form of energy Lysosomes • Also known as the stomach or trash can of the cell • It contains the cells digestive enzymes Ribosomes • Ribosomes make proteins which contain genetic information • The ribosome is made in the nucleolus The Golgi Apparatus • Packages proteins for export by the cell • Similar to factory workers • Appear as flattened sacks Microtubules • Pass information from the nucleus to other parts of the cells • Microtubules act as telephone wires Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum • Makes steroids and regulates calcium levels • Breaks down toxic substances • Smooth ER acts like a factory Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Moves proteins through the cell • Rough ER acts as delivery trucks • Rough ER are covered in ribosomes Cell Membrane • Selectively permeable / semipermeable • Lipid bi-layer (2) • Controls what enters and leaves the cell • Found in both plant and animal cells The Plant Cell • Contains many of the same organelles as the animal cells • Characterized by its square shape, chloroplast, and central vacuole The Cell Wall • Help plants to keep their shape and offers protection • Made of cellulose, a carbohydrate Chloroplast • Uses light energy to make sugars (food for plants) • The site of photosynthesis • Contains chlorophyll which gives plants their green color Vacuole • Stores water, nutrients and wastes • The largest organelle found in the plant cell The Eukaryotic Cell