* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3-CellStructure
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
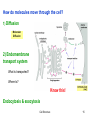
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
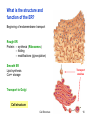
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
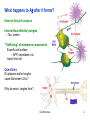
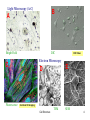
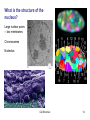
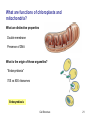
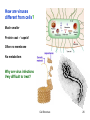
Chapter 4: Cell Structure Topics you are not responsible for: Bacterial cell walls and the Archaea Cell-to-cell interactions End of Chapter questions: Understand: all Apply: all Synthesize: 1, 3, 4 Do all mQuiz questions Inner Life of The Cell TEM of Platinum/Carbon replicas of HeLa cell cytoplasm showing clathrincoated vesicles and microtubules Cell Structure 1 What happens to Ab after it forms? External Amyloid plaques Internal Neurofibrillary tangles -- Tau protein “Trafficking” of membrane components Exportto cell surface -- APP, secretases, etc. Import into cell Questions Do plaques and/or tangles cause Alzheimer’s Dis.? Why do neuro. tangles form? Cell Structure 2 Cells of you immune system circulate continuously through your body Circulation of cells and Interstitial fluid -- antigens / pathogens -- immune cells Cell extravasation -- Chemokines -- receptors -- adhesion proteins Leukocyte Rolling Leukocyte Homing Cells and Organs 3 Light Microscopy (A-C) B A Bright Field DIC Electron Microscopy C Fluorescence DIC Video E D Confocal 3D imaging Cell Structure TEM SEM 4 Microscopy Normal Light Microscopy DIC $$ Tick and Sick-2 Keratocyte Dance 5 Microscopy, cont Fluorescence $$$ Confocal $$$$ Tick and Sick-2 6 Electron Microscopy SEM vs TEM $$$$$ Tick and Sick-2 7 Examples of Light Microscopy Examples of Electron Microscopy A. Standard Bright Field Microscopy of Histological section of brain stained to show Neurofibrillary Tangles (>) and Aβ plaques (*). http://www.microscopy- D. TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy) of neurons (crosssection) showing internal cellular structures. ttp://visualsunlimited.photoshelter. uk.org.uk/mag //artsep06/mc-Alzheimer.html com/image/I00005SIGjGWwl9U B. DIC (Differential Interference Microscopy) of Neocortical neurons in primary culture. Note accentuation of edges and 3D-like appearance Adapted from http://www.ipmc.cnrs.fr/cgibin/standard.cgi?descriptif=mantegazza.txt&dossier 1=equipes&dossier2=mantegazza&site=inter&men u=1&ssmenu=14&lang=uk E. SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) of neurons showing external surface structures. http://www.med.nus.edu.sg/ant/histonet/txt/nervs em/nerv03.sem.html C. Fluorescence Microscopy of fibroblast cell culture stained for proteins of the nucleus, mitochondria, and peroxisomes, as well as the filamentous actin and intermediate filaments. http://learn.hamamatsu.com/galleries/ digitalimages/muntjac/muntjaclarge10.html Cell Structure 8 Growing Cells Advantages over whole organism •Individual cell type •Controlled conditions •Easier analysis •Stem cell culture & tissue regeneration Limitations •Individual cell type •Genetic changes Tick and Sick-2 9 How do Eukaryotic cells differ from Prokaryotic cells? Prokaryotes = bacteria Eukaryotes = everything else Size Cytoplasm organization Structure of chromosomes We will discuss other differences later Eukaryotic cell cytoplasm Cell Structure 10 How big are cells? How Big is It? Why are cells so small? Surface to volume (S/V) ratio Cell Structure 11 What are some functional regions of cells? Cytoplasm Cell membrane (plasma membrane) Extracellular structures Cell wall Cilia & flagella EC matrix Cell Structure 12 What are the components of eukaryotic cytoplasm? Membrane bound compartments -- Cytoplasm vs “cytosol” Molecular building blocks Proteins/enzymes -- Cytoskeleton Ribosomes Cell Structure 13 What is the structure of the nucleus? Large nuclear pores -- two membranes Chromosomes Nucleolus Cell Structure 14 How do molecules move through the cell? 1) Diffusion Molecular Diffusion 2) Endomembrane transport system What is transported? Where to? Know this! Endocytosis & exocytosis Cell Structure 15 What is the structure and function of the ER? Beginning of endomembrane transport Rough ER Protein: -- synthesis (Ribosomes) -- folding -- modifications (glycosylation) Smooth ER Lipid synthesis Ca++ storage Transport vesicles Transport to Golgi Cell structure Cell Structure 16 What is the structure & function of the Golgi? Protein modifications -- e.g., glycosylation Sorting & Packaging into vesicles How are proteins transported Through the Golgi? View these animation Virtual cell -- Protein Trafficking Virtual cell – Protein modification Links on Class resource page Cell Structure 17 How are proteins modified within the golgi? How are enzymes ‘tagged’ for transport to lysosomes? -- hydrolytic enzymes -- NAcGluAm-P transferase -- mannose-6-P -- M-6-P receptors Intracellular Transport 18 What is the function of lysosomes? Breakdown of: Intracellular materials Extracellular materials How are materials transported to lysosome? Hydrolases from Golgi Materials from inside and outside the cells Cell Structure 19 Mutations to transport processes underlie some genetic diseases Lymphocytes of Mucolipidosis II I-cell diseases Accumulation of lysosomes Mental retardation Metabolic abnormalities Fatal Mucolipidosis II NAcGluAm-P transferase deficiency What is expected effect? Tay-Sacks disease ganglioside GM2 lipase deficiency -- lipid recycled from cell surface What is expected effect? Cell Structure 20 What are functions of chloroplasts and mitochondria? What are distinctive properties Double membrane Presence of DNA What is the origin of these organelles? “Endosymbiosis” 70S vs 80S ribosomes Endosymbiosis Cell Structure 21 What proteins comprise the cell cytoskeleton? Intermediate filaments Microtubules Actin filaments How is the “cytoskeleton” different from a animal skeleton? Organization and function of Intermediate filaments Mechanical strength Cell Structure 22 What are the organization and functions of microtubules? cytoplasmic transport chromosome movements movements of flagella and cilia -- “9+2” structure Cytoplasmic streaming Closer view on microtubules Cell Structure Flagella Cilia 23 What are the organization and functions of actin filaments? Various types of cell movements Membrane contractions muscle contraction Crawling motions Interacts with “myosin” Membrane ruffling Cell Structure Heart Cell 24 How do plant cells differ from animal cells? Chloroplasts Cell Wall Vacuole Cell Structure 25 How are viruses different from cells? Much smaller Protein coat – ‘capsid’ Often no membrane No metabolism Why are virus infections Very difficult to treat? Cell Structure 26