* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Reproduction
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
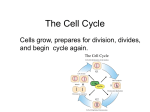
Cell Reproduction Cell Growth Increase in: Limited amount Size = Number = Most growth Mitosis = the process in which a Eukaryotic cell divides itself into two equal, genetically identical parts Mitosis Five Phases 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Interphase 1. Stage of cell growth 2. All organelles reproduce. 3. Chromosomes duplicate themselves. 4. The cell spends most (90%)of its time in this phase. 5. The cell cycle is at rest in this phase. http://fermat.stmarys-ca.edu/~jpolos/science/telophase.html Copyright John Polos January 21, 1999 Interphase Prophase 1. Chromosomes start to become visible 2. Nucleolus disappears 3. Centrioles move apart 4. Centrolies start to produce the spindle 5. Nuclear Envelope disappears Prophase Metaphase 1. Centrioles are lined up at opposite ends (poles) of the cell. 2. Chromosomes are lined up across the middle of the cell in identical pairs. 3. The Spindle has connected the daughter chromosomes to the poles. Metaphase Anaphase 1. "Daughter" chromosomes begin moving to opposite poles. 2. Spindle fibers get shorter. 3. By the end, each pole has equal number of identical chromosomes . Anaphase Telophase 1. The spindle starts to dissolve 2. The nuclear envelope starts to reform. 3. The cell membrane starts to close together in the center of what was the old cell, forming 2 new cells. (Cytokinesis) http://fermat.stmarys-ca.edu/~jpolos/science/telophase.html Copyright John Polos January 21, 1999 Telophase Telophase (complete) Interphase http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase http://www.bioweb.uncc.edu/biol1110/Stages.htm