* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (1.2) Cell Division (p22-27)
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
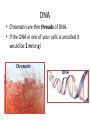
(1.2) Cell Division (p22-27) Cell Division • Cells must divide to survive. • There is a limit to how large a cell can grow. • If the amount of material in a cell is too large the cell dies. Cell Division When a cell divides - two new cells are created - each cell is identical to the original cell The set of instructions each cell inherits is stored in a unique molecule called DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). DNA • DNA in the nucleus of the cell contains the hereditary material. • DNA molecules have a shape like that of a ladder. • To fit inside the nucleus DNA forms compact coiled threads called chromatin. • To reproduce the chromatin packs together to form chromosomes. • Chromosomes pass on hereditary information when a cell divides. DNA • Chromatin are thin threads of DNA. • If the DNA in one of your cells is uncoiled it would be 2 m long! Chromatin DNA Cell Cycle • The series of events in the life of a cell is called the cell cycle. • Two main stages: i) growth - called interphase ii) division - consisting of mitosis and cytokinesis Growth Stage • During interphase the cell: - grows - carries out its usual functions - makes copies of its DNA and organelles to prepare for cell division • Most cells spend most of their lives in interphase. • Interphase ends when a cell begins to divide. Division Stage Two phases of cell division: 1. Mitosis - the contents of the nucleus separate into 2 identical copies. 2. Cytokinesis - cytoplasm and organelles divide into 2 identical, separate copies - each cell now starts its own cell cycle Cell Division - It’s Important Through cell division livings things undergo three important functions: i) growth ii) maintenance iii) repair Classwork Text • p 23 LC #1-3 • p 25 LC #1-3 • p 27 LC #1,3 Quiz: Next class on section (1.1) - cell parts, diffusion and osmosis