* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Outer boundary of the cell, which regulates what, enters and exits
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
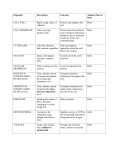
Outer boundary of the cell, which regulates what enters and exits the cell. It is selectively permeable. Cell membrane This is the jelly-like fluid matrix within the cell Cytoplasm The organelle that releases energy from stored food molecules mitochondrion Site of protein synthesis (where proteins are made) Ribosome Structures within the cell that perform specialized functions organelles Controls all cell activities, especially growth and reproduction nucleus Porous double membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm Nuclear envelope Network of protein filaments that helps the cell to maintain its shape cytoskeleton Genetic material that is found in the nucleus of a nondividing cell Chromatin Compact form of DNA and protein in the nucleus of a cell about to divide Chromosome Set of tubular passageways involved with the transport of proteins; it has many ribosomes attached and connects the nucleus to the cell membrane Rough endoplasmic reticulum Non-living layer that surrounds a plant cell and provides protection and support Cell wall Tubular structures found only in animal cells that are involved in cell division Centrioles Storage sacs that store food, water, salts and other materials Vacuoles Stack of flattened membranes that processes and packages proteins to be secreted out of the cell Golgi apparatus Organelles that contain powerful digestive enzymes that break down substances to be used by the cell as well as toxic materials Lysosome Site of photosynthesis in the plant cell Chloroplast Tubular passageways that have few or no ribosomes attached and is the site of lipid synthesis Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Tail-like structure found in prokaryotes and some animal cells; used for cell movement flagella