* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endoplasmic Reticulum - Brandywine School District
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
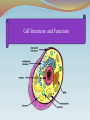
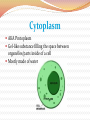
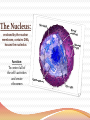
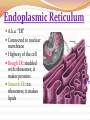
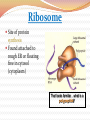
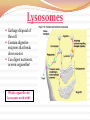
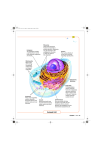
Cell Structures and Functions •Boundary of the cell •Keeps all parts of the cell inside (bi-level phospholipid layer) •Has openings where items may enter and exit cell (aided by protein transports) Cytoplasm AKA Protoplasm Gel-like substance filling the space between organelles/parts inside of a cell Mostly made of water The Nucleus: enclosed by the nuclear membrane, contains DNA, houses the nucleolus Function: To control all of the cell’s activities and create ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum A.k.a. “ER” Connected to nuclear membrane Highway of the cell Rough ER: studded with ribosomes; it makes proteins Smooth ER: no ribosomes; it makes lipids Ribosome Site of protein synthesis Found attached to rough ER or floating free in cytosol (cytoplasm) That looks familiar…what is a polypeptide? GOLGI COMPLEX (Apparatus) Shaped like a stack of pancakes Has a job similar to ER Packages together simple molecules to be stored in vesicles to be used later or expelled from the cell Creates lysosomes Lysosomes Garbage disposal of the cell Contain digestive enzymes that break down wastes Can digest nutrients, or even organelles! Which organelles do lysosomes work with? •Power Houses of the cell •Act like our digestive system (takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and creates energy for the cell - cellular respiration) Vacuoles •Storage bubbles in the cell •Can house nutrients, wastes, or excess water form the cell http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/plantcell.html http://www.fossweb.com/modulesMS/DiversityofLife/index.html http://www.nsf.gov/news/overviews/biology/interactive.jsp http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio104/cells.htm http://cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_main.html Cell Membrane (red) Nucleoplasm (yellow) Mitochondria (red) Lysosome (pink) - Cytoplasm (leave white) Microtubules (brown) Ribosome (blue) Nucleolus (gray) Golgi Apparatus (purple) Smooth Endoplasmic - Reticulum (green) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (orange) Nuclear Membrane (dark brown) -