* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proteins
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
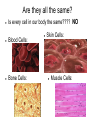
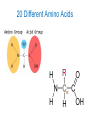
PROTEINS This ¼ of “THE BIG FOUR” makes YOU... YOU! Macromolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Fat Proteins Sugar and Starch UMMMMM.... ALMOST EVERYTHING ELSE! Nucleic Acids DNA and RNA Proteins I lift things up.... Got Beef? Oops... I meant Chicken.... or maybe, fish... or beans... or.... What happens when... You munch on that Big Mac??? Does it go sloshing around, in big chunks, through your veins? NO! Everything you eat MUST BE Digested... Why must STARCH be digested??? Why must EVERYTHING be digested??? - So that it can DIFFUSE through the cell membrane Think about the NYS lab... What was the purpose of the lab??? - To model DIFFUSION (molecules moving from high to low concentration) What is the chemical reaction that uses water to destroy a bond in order to perform digestion??? - Hydrolysis Remember: Diffusion Through A Membrane The initial set up The “Cell” filled with glucose and starch solutions Water & Iodine in the beaker cover the “cell” What Happened???? And... WHY?????? Final State: What Color is the Cell Now? BLACK! What does that mean? IODINE DIFFUSED IN! Things Need to Be Digested Each cell must have a constant supply of different monomers in order to make the polymers it requires! The food we eat must be broken down so that it is small enough to fit through the cell membrane… THEN, the cell uses those micromolecules to make macromolecules! So.... Every time Mrs. C. falls... And needs to make new skin cells and muscle cells to heal what has been injured... She needs PROTEINS! Are they all the same? Is every cell in our body the same???? NO Blood Cells: Bone Cells: Skin Cells: Muscle Cells: Different... Yet, Similar... Even though they are VERY different... EVERY cell in your body has proteins in them... and the proteins are different because the shape and function of the cell are different! BUT, BUT, BUT! ALL proteins are made up of the same 20 Amino Acids! Just like our alphabet... 26 letters make up thousands of words! Your Mission (should you choose to accept it...) Create a unique protein.... “Modeling” DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS BTW... WHAT IS DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS ????? - Removing a water molecule to create a bond to build something more complex! Proteins Made of C, H, O and N Are a long polymer chains of Amino Acids (monomers) The Amino Acids are bonded in a specific sequence and fold into a specific shape! 20 Different Amino Acids Amino Acids Make Proteins… How do we GET Amino Acids? Nutrition (Yup…. Part of STRANGER-C!) We Digest the food we consume. Hydrolysis (and other chemical reactions) break down the polymers into small monomers. Why? So the monomers can DIFFUSE into the cell. Why? So the cell can SYNTHESIZE polymers again! Where/How are proteins made? • Proteins (polypeptides) are made at the RIBOSOME • The ribosome bonds amino acids together to make whichever protein the cell needs • How does the ribosome know which protein to make? DNA!