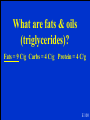* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry Jeopardy C.P. Bio.
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
THIS IS A Biochemistry Review Intro to Biochem Carbs Proteins Lipids Nutrients 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Mystery “Biology” literally means this. A 100 What is the study of life? A 100 The type of bond seen below. C=C A 200 What is a double bond? A 200 These are the 6 elements which are the basis of Biochemistry. A 300 What are C, H, O, N, P, S? (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur) A 300 One type of chemical formula is known as the molecular formulas (C6H12O6). The following are examples of another kind of chemical formula. A 400 What is a structural formula? A 400 Polymers can be formed by this process. A 500 What is a condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis)? A 500 They are the monomers of carbohydrates. B 100 What are monosaccharides? B 100 The common ratio of H:O for carbohydrates is this B 200 What is 2:1? B 200 The function of starch in a plant. B 300 What is the main carbohydrate storage product in plants? B 300 The disaccharide named Maltose is formed by chemically bonding two of these monosaccharides. B 400 What is glucose? B 400 Glucose, Galactose and Fructose have the same chemical formula but different structures. B 500 What are isomers? B 500 The monomers of proteins. C 100 What are amino acids? C 100 Amino acids that are non-essential. C 200 What are amino acids made by the body? C 200 Where is the carboxyl group in an amino acid? C 300 What is “c”? C 300 DAILY DOUBLE C 400 The function of enzymes (proteins) is this C 400 What is to control the rate of reaction by acting as catalysts? C 400 This is an example of a structural protein found in the human body. C 500 What are keratin (found in hair an nails), and collagen proteins (found in skin, muscles, & joints)? C 500 The monomers of triglycerides. D 100 What are glycerol & fatty acids? D 100 The following is this kind of fatty acid D 200 What is unsaturated? D 200 The cell membrane is composed of this type of lipids D 300 What are phospholipids? (Phospholipids bilayer) D 300 Cholesterol is an example of this type of lipid. D 400 What are steroids? D 400 A reason that trans fats are so popular in food production. D 500 What is: • they produce a spreadable product? • they are cheap? • they have a long shelf life? D 500 The nutrient with the most calories. E 100 What are fats & oils (triglycerides)? Fats = 9 C/g Carbs = 4 C/g Protein = 4 C/g E 100 The most abundant inorganic nutrient (compound) in living organisms. E 200 What is water? E 200 The reason some compounds are considered organic. E 300 What is they contain carbon? (bonded at least to hydrogen and oxygen) E 300 “Beriberi,” and “scurvy” are examples of “deficiency disorders” that happen to people who don’t consume enough of this kind of nutrient. (one word) E 400 What is are vitamins? E 400 The problem with swallowing too much of the fat soluble vitamins such as A, D or E. E 500 They can build up in to body to toxic levels? E 500 Chitin is found in the exoskeleton of animals known as Arthropods. This group includes these kinds of animals. F 100 What are crustaceans, arachnids and insects? F 100 There are this many electrons in the outer shell of carbon F 200 What is four (4)? F 200 Testosterone and estrogen are examples of this lipid. F 300 What is a steroid? F 300 Proteins of many monomers are also known by this name. F 500 What is polypeptides? F 500 This polysaccharide provides calories for some animals, and no calories for others. F 400 What is cellulose? F 400 The Final Jeopardy Category is: Protein Please record your wager. Click on screen to begin Protein such as insulin and growth hormone, that regulate certain processes in the human body, are known as this type of protein. Click on screen to continue What is regulatory protein? Click on screen to continue Thank You for Playing Jeopardy! Game Designed By C. Harr-MAIT