* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download List what you think is necessary in order for something to be
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
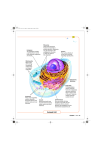
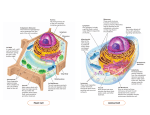
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living things. How small are cells? Some Random Cell Facts • The average human being is composed of around 100 Trillion individual cells!!! • It would take as many as 50 cells to cover the area of a dot on the letter “i” WOW!!! What are “Organelles” ? Organelles of the Animal Cell • Ribosomes • Chromosomes • Nucleus • Vacuole • Cytoplasm • Cell Membrane • Endoplasmic Reticulum • Mitochondria • Lysosome • Golgi apparatus All Cells •Have organelles •Cell Membrane •Cytoplasm •DNA CELL MEMBRANEIN PLANT CELLS- found just inside the cell wall. IN ANIMAL CELLS – It is the outer covering of the cell. It has tiny openings or pores that control the movement in and out of the cell. It is selectively permeable. Cytoplasm • Region between the nucleus and cell membrane – Clear, thick jelly-like substance – Constantly moving – Contains many important organelles DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid •Found in all cells •Carries genetic(hereditary) information •Controls activities of the cell •Usually found in nucleus Plant and Animal Cells Jane Horstmann Plant or animal cell? How can you tell? This is an animal cell because _______________. More pictures of cells Two Kinds of Cells • Prokaryotic: without a nucleus • Eukaryotic: with a nucleus Prokaryotes •Single cell, without a nucleus or membrane bound organelles •Most common - Bacteria Eukaryotic • All protists are eukaryotes most are unicellular • Multicellular – many cells • Can see with your eye • Animals, Plants • Fungi – mushrooms and yeast Cell Structures, Functions and Transport Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Go to Section: Cell Membrane Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 1. Nucleus – Nickname: “The Control Center” – Function: holds the DNA – Parts: Nucleolus: dark spot in the middle of the nucleus that helps make ribosomes Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 2. Ribosomes – Function: makes proteins • • • – – Grain like Made by the nucleolus Made of RNA (ribonucleic acid) – RNA –directs the production of protiens. This is controlled by DNA Found in all cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic Location: endoplasmic reticulum or cytoplasm Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 3. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) – Nickname: “Roads” – Function: Transport system that carries proteins throughout the cell. • tubular • leading out from the nuclear membrane throughout the cell. • May go out to the cell membrane Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum DELIVERY SYSTEM OF THE CELL 2 Types: 1.Rough ER: –Rough appearance because it has ribosomes –Function: helps make proteins, that’s why it has ribosomes 2.Smooth ER: –NO ribosomes –Function: makes fats or lipids Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 4. Golgi Complex – Nickname: The shippers – Function: packages, modifies, and transports materials to different location inside/outside of the cell – Appearance: stack of pancakes Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Go to Section: Ribosomes Cell Membrane Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 5. Lysosomes: small and circular, but bigger than ribosomes – Nickname: “Clean-up Crews” – Function: to break down food into particles the rest of the cell can use and to destroy old cells – Common in animal cells but rare in plant cells Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Animal Cell Section 7-2 Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosomes Cell Membrane Mitochondria Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 6. Mitochondria – – Nickname: “The Powerhouse” Function: Supplies most of the energy for the cell • Breaks down food (glucose) into water and carbon dioxide, which releases energy. This is called respiration – – – stores energy more active a cell is the more mitochondria it will have Has small amount of DNA. Scientist believe they were once free living organisms that invaded the cell millions of years ago. Animal Cell Cytoplasm Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosomes Cell Membrane Mitochondria Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum • Now let’s talk about structures only found in PLANT Cells!! Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 7. Vacuoles – Function: stores water • This is what makes lettuce crisp – When there is no water, the plant wilts – Plants often have one or two very large ones – Animals have small and few Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 8. Chloroplasts – Function: traps energy from the sun to produce food for the plant cell – Process is called photosynthesis • Equation for photosynthesis Carbon dioxide + water Glucose + oxygen 6CO2 6O2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + Chloroplasts Figure 7-5 Plant and Animal Cells Plant Cell Section 7-2 Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Cell Wall Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Function 9. Cell Wall – Function: strong, rigid; made of cellulose, provides support and protection to the cell membrane, allows materials (carbon dioxide, water, oxygen, and other dissolved materials) to pass in and out – Found outside the cell membrane in plant cells Plant Cell Cytoplasm Vacuole Smooth ER Ribosomes Chloroplasts Cell Membrane Cell Wall Nucleolus Golgi Bodies Nucleus Mitochondria Rough ER How Are They Different? Plant Cell • cell wall and cell membrane • rectangular shape • large vacuole • makes glucose – contains chloroplasts which make chlorophyll - which is used for photosynthesis Animal Cell • cell membrane • oval or round shape • small vacuoles Comparing Plant and Animal Cells Plant Animal