* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Membranes Dr. Imrana Ehsan
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Type three secretion system wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
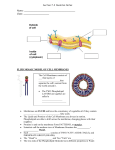
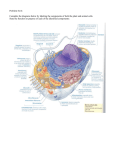
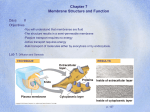
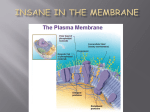
CELL MEMBRANE DR.IMRANA EHSAN Structure and function of cell components (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Membranes Cytoskeleton The plasma membrane is the boundary that separates the living cell from its nonliving surroundings The plasma membrane exhibits selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others • Many organelles contain or are enclosed by membranes, including ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Plasma membrane Mitochondria Chloroplasts Nuclear envelope Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Microbodies (aka perioxisomes) Cell membranes Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, containing hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions The fluid mosaic model states that a membrane is a fluid structure with a “mosaic”membranes of various proteins in Cellular are embedded fluid it. mosaics of lipids and proteins Structure of cell membrane Phospholipids in the plasma membrane can move within the bilayer Most of the lipids, and some proteins, drift laterally Rarely does a molecule flip-flop transversely across the membrane The Fluidity of Membranes As temperatures cool, membranes switch from a fluid state to a solid state The temperature at which a membrane solidifies depends on the types of lipids Membranes rich in unsaturated fatty acids are more fluid than those rich in saturated fatty acids Membranes must be fluid to work properly; they are usually about as fluid as salad oil As temperatures cool, membranes switch from a fluid state to a solid state The temperature at which a membrane solidifies depends on the types of lipids Membranes rich in unsaturated fatty acids are more fluid than those rich in saturated fatty acids Membranes must be fluid to work properly; they are usually about as fluid as salad oil Based on the functions of the above organelles / membranes write down some of the roles of the membranes in the cells (Leave some space as we will be adding to this list) Role of Cell Membranes Structure of Cell membranes Fluid Mosaic Model Electron micrograph of cell membrane Lipids ◦ Remember lipids have hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails ◦ To avoid the hydrophobic tails coming in contact with water a continuous bilayer sphere is formed. ◦ Therefore hydrophobic interactions hold membranes together Structure of Cell membranes Proteins ◦ Integral proteins (intrinsic) Proteins that are embedded in the membrane They are held in place by hydrophobic interactions (integral proteins have hydrophobic groups on their outer surface) ◦ Peripheral proteins (extrinsic) Proteins attached to the surface of the membrane (often forming non-covalent bonds with integral proteins) Structure of Cell Membranes Proteins cont… ◦ Phospholipid bilayer Forms boundary to isolate cell contents from environment Restricts passage of hydrophilic substances across the membrane ◦ Cholesterol Increases bilayer strength, flexibility Reduces membrane fluidity Reduces permeability to water-soluble substances Function of membranes macromolecules Some proteins in the plasma membrane can drift within the bilayer Proteins are much larger than lipids and move more slowly Attachment ◦ Cytoskeleton ◦ Extracellular matrix Intercellular Junctions ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Plasmodesmata Tight Junctions Gap Junctions Desmosomes Function of Membrane Proteins Transport ◦ Carrier Proteins ◦ Channel Proteins Receptors Enzymes Cell to Cell recognition Function of Membrane Proteins Function of membrane protiens Integral (Membrane-spanning or intrinsic) •Can span membrane several times •Either move around or are kept in place by cytoskeleton proteins Allows for cell polarity Associated (peripheral or extrinsic) •Loosely bound to membrane •Enzymes and structural proteins • Use all resources to find out more about the functions of membrane proteins. Based on the functions of proteins, add to your list on the role of membranes in cells Learning Activities