* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plama Membrane
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
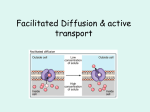
PLASMA MEMBRANE FUNCTIONS OF THE PLASMA MEMBRANE 1. Provides a boundary between a cell and its environment 2. Controls the flow of material in and out of the cell A. The membrane is selectively permeable, which means that it lets some substances pass through, but not everything. (selective) 3. Maintains homeostasis: balance within the cells A. Allows more water and food to come in when needed, gets rid of what is not needed RELATING THE STRUCTURE TO ITS FUNCTION 1. The membrane is a bilayer (2 layers). 2. Made up molecules which are a glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acids, and a phosphate group; called the phospholipid bilayer. 3. The polar head and nonpolar tail – fatty areas that attract and repel water. A. make the membrane behave like a fluid 4. Embedded proteins: determine which molecules can go in and out of the cell. A. Proteins serve as recognition markers B. Carbohydrates serve as cell identification tags THE FLUID MOSAIC MODEL The phospholipid bilayer allows other molecules to “float” in the membrane. Think of the phospholipids in the bilayer as creating a “sea” where other molecules can float on top, like a barrel of apples floating on top of the water. PROTEINS IN THE PLASMA MEMBRANE Transmit signals inside the cell Act as a support structure Provide pathways for substances to enter and leave. CHOLESTEROL IN THE PLASMA MEMBRANE Prevents fatty acid tails from sticking together CARBOHYDRATES IN THE PLASMA MEMBRANE Identify chemical signals PASSIVE TRANSPORT 1. Passive Transport - Particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. A. Cell does not require an input of energy . B. “Facilitated diffusion” C. Ex. When you leave the classroom you will all go the same direction down the hallway (ex. Diffusion) •There • • • are 3 modes of passive transport: 1. Diffusion 2. Facilitated Diffusion 3. Osmosis DIFFUSION Diffusion – the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration A. Difference in the concentration is called a gradient Initial Conditions: Diffusion takes place: DIFFUSION IN A CELL FACILITATED DIFFUSION FACILITATED DIFFUSION -THE MOVEMENT OF MATERIALS ACROSS THE PLASMA MEMBRANE USING PROTEINS. Channel Proteins Carrier Proteins OSMOSIS OSMOSIS Osmosis – the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. 3 TYPES OF SOLUTIONS: 1. Isotonic 2. Hypotonic 3. Hypertonic ISOTONIC SOLUTIONS A. Solutions where the concentration of solutes and water is equal to/the same as the normal cells of the body and the blood B. Movement into the cell = movement out of the cell: water moves in both directions (in and out) HYPOTONIC SOLUTION A. Concentration of solute (salt) is lower in normal cells of the body and blood. B. Water will move into the cell to equalize C. Increases osmotic pressure: pressure that’s generated as the water flows through the plasma membrane D. Cell could burst if it takes in too much water. HYPERTONIC SOLUTIONS A. Concentration of the solute outside of the cell is higher than inside the cell. B. Water rushes out of the cell C. Can result in the cell shrinking – water goes out of plant cell causing it to wilt ACTIVE TRANSPORT Move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration – transport against the gradient A. Requires energy to move items into the cell B. Ex. Everyone going down the hallway in the same direction except for you, must exert energy to get past everyone. ACTIVE TRANSPORT USING CARRIER PROTEINS TYPES OF ACTIVE TRANSPORT PUMPS Na+/K+ ATPase pump Moves three Na+ ions out of the cell and two K + ions into the cell to maintain the level of these ions inside and outside of the cell. ADD DEMONSTRATION OF NA/K PUMP HERE Active Transport: Na+/K+ Pump ATPase pump protein gets phosphorylated by ATP. Protein’s conformation changes... causing binding & then release of ions. ENDOCYTOSIS The process by which the cell surrounds and takes particles into the cell. Phagocytosiscellular eating Pinocytosiscellular drinking EXOCYTOSIS Secretion of material out of the cell through the plasma membrane Example: when you yawn or cry, the tear ducts export salt from the glands COMPARING ENDOCYTOSIS AND EXOCYTOSIS Endocytosis: Surrounds and takes substances into the cell Transports substances too large to move across the plasma membrane Exocytosis: Surrounds and expels or secretes substances