* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Major Cell Parts and Organelles
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
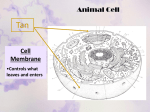
Major Cell Parts and Organelles Plasma membrane (a.k.a. cell membrane) Surrounds cell - keeps contents separated from surroundings Has protein channels & pores which let things in and out Cell Wall Outermost structure of a plant Cellulose Dead Gives support and shape Cytoplasm (cell - jelly like substance) Holds all the organelles Maintains internal environment (reminder - all cells have this) Cytoskeleton Network of fibers giving: Shape Support Place where movement of cell parts can occur within cell Nucleus Information center of cell Stores genes (as chromosomes) Yeast cell nucleus nuclear pores NUCLEUS Two membranes of nuclear envelope Chromatin Nucleolus Pore ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Ribosomes Figure 4.6 Chromosomes Contain 30,000 - 40,000 genes Genes code for traits (eye color, height, etc.) Mitochondria Changes food (glucose) into usable energy (ATP) Endoplasmic Reticulum Channels of membranes used for transporting materials 2 Types: Rough - ribosomes attached 1) Ø 2) Proteins for export Smooth - no ribosomes attached Ø Lipids and carbohydrates Rough ER Transport vesicle buds off 4 Ribosome Sugar chain 3 Secretory (glyco-) protein inside transport vesicle Glycoprotein 1 Polypeptide 2 ROUGH ER SMOOTH ER ROUGH ER Nuclear envelope Ribosomes SMOOTH ER Figure 4.9 ROUGH ER Nucleolus Produces Ribosomes Found within nucleus • NucleOLus QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Ribosomes Initiates or begins the synthesis of proteins • If free - protein stays in cell • If attached to ER - protein leaves cell Golgi Apparatus Packaging and distribution center Into a membrane bound package called a vesicle….. Modifies, sorts, and ships products Especially proteins 0% Vesicle Lysosomes (to burst or destroy bodies) Sac of digestive enzymes Digests used cell parts and invaders Recycles parts of destroyed “things” Rough ER Transport vesicle (containing inactive hydrolytic enzymes) Plasma membrane Golgi apparatus Engulfment of particle Lysosome engulfing damaged organelle “Food” LYSOSOMES Food vacuole Figure 4.11B Digestion Central Vacuole WATER and salts storage Large in plants Helps give plants support Central vacuole Nucleus Figure 4.13A Chloroplasts In plants only Converts energy from sun into food (glucose)