* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eukaryotic Cell Structure
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
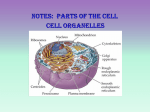
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Cell Wall Found in cells of plants, fungi, bacteria, and some protists. Fairly rigid structure found outside the cell membrane. Cell Wall Provides additional support and protection. Cell walls in plants are very porous which allows molecules to pass through (not selective). Nucleus Contains strands of DNA called chromatin. When the cell divides, chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. Controls the activity of organelles by controlling protein production. Contains an organelle called the nucleolus which makes ribosomes. Ribosomes Where proteins are made. Has no membrane. Formed of RNA and proteins. During protein synthesis, ribosomes and RNA translated from DNA leave the nucleus through the nuclear envelope and enter the cytoplasm Nuclear Envelope Separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. Double membrane. Made up of two phospholipid bilayers containing small nuclear pores for substances to pass through. Cytoplasm Clear, gelatinous fluid inside a cell. Suspends organelles such as ER, golgi apparatus, vacuoles, lysosomes, chloroplasts, plastids, mitochondria, and centrioles. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Site of cellular chemical reactions. Arranged in a series of highly folded membranes. These folds allow a large amount of ER to do work in a small amount of space. Rough ER vs Smooth ER Rough ER Areas of ER where ribosomes are attached to the surface and carry out protein synthesis. Smooth ER Areas of the ER not studded with ribosomes. Involved in numerous biochemical activities, including production and storage of lipids. Golgi Apparatus Flattened stack of tubular membranes that modify proteins. After proteins are made by ribosomes, they are transferred to the golgi apparatus. Golgi Apparatus Sorts proteins into packages and then packs them into membrane-bound structures called vesicles to be sent to the appropriate destination. Vacuoles Membrane bound compartments or sacs. Temporarily store materials such as food, wastes, and enzymes. Not usually present in animal cells. When they are present in animal cells, they are very small. Lysosomes Organelles that contain digestive enzymes. Digest worn-out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses and bacteria. Has a membrane which prevents the digestive enzymes from destroying the cell. Lysosomes Can fuse with vacuoles and dispense enzymes into the vacuole, digesting its contents. Sometimes lysosomes digest the cells that contain them as in the case of a tadpole tail. Chloroplasts Located in the cells of green plants and some protists. Capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy. Store the chemical energy in bonds of sugar molecules. Belong to a group of plant organelles called plastids. Chloroplasts Has a double membrane. Inner membranes are called thylakoid membranes and are arranged in stacks of membranous sacs called grana which trap sunlight. Fluid that surrounds the stacks of grana is called stroma. Plastids Store materials such as starches, lipids, and pigments. Named according to their color or the pigment they contain. Chloroplasts contain the green pigment chlorophyll which traps light energy. Mitochondria Membrane bound organelles in plant and animal cells which transform energy for the cell. Have an outer membrane and highly folded inner membrane where energy storing molecules are produced. Energy is then stored in bonds of other molecules that cell organelles can access easily and quickly when energy is needed. Cytoskeleton Network of tiny rods and filaments. Microtubules Thin hollow cylinders made of protein. Microfilaments Smaller solid protein fibers. Cytoskeleton Forms a framework or structure for the cell. Can be dismantled in one place and reassembled somewhere else in the cell, changing the cell’s shape. Cytoskeleton Anchors and supports many organelles. Provides a highway system through which materials move within the cell. Centrioles Found in cells of animals and most protists. Occur in pairs. Made up of microtubules. Play an important role in cell division. Cilia and Flagella Organelles made of microtubules. Aid in locomotion and/or feeding. Major means of locomotion in single celled organisms. Cilia and Flagella Cilia Short, numerous projections that look like hairs. Motion similar to oars in a rowboat. Cilia and Flagella Flagella Long projections. Move with a whip-like motion. Cells usually only have one or two.