* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12.3 Transcription and Translation PPT
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
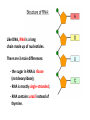
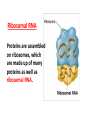
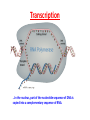
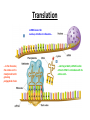
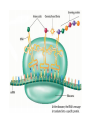
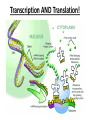
CH 12.3 RNA & Protein Synthesis Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within the cell… …just how are those instructions decoded??? Step 1: …by copying the nucleotide sequence of DNA into RNA: ribonucleic acid! Like DNA, RNA is a long chain made up of nucleotides. There are 3 main differences: - the sugar in RNA is ribose (not deoxyribose); - RNA is mostly single-stranded; - RNA contains uracil instead of thymine. Types of RNA Messenger RNA Messenger RNA Carries copies of gene instructions (to synthesize proteins out of amino acids) from DNA to the rest of the cell. Ribosomal RNA Proteins are assembled on ribosomes, which are made up of many proteins as well as ribosomal RNA. Transfer RNA Transfer RNA delivers each amino acid coded for by messenger RNA to the ribosome for protein assembly. Transcription …In the nucleus, part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence of RNA. • RNA polymerase opens up DNA and separates the strands. • RNA polymerase uses one DNA strand as a template to produce a strand of RNA. • RNA polymerase binds only to promoters, special DNA regions with specific base sequences that indicate where to start and stop transcription. Can YOU transcribe? RNA strand: A U U G A C U G A A C U G A DNA strand: T A A C T G A C T T G A C T REMEMBER: in transcription, uracil replaces thymine in RNA! Translation: Breaking the genetic code Translation is the process of decoding mRNA nucleotides into proteins • Proteins are made by joining amino acids into long chains called polypeptides. • The order of these amino acids determines which protein is made. • The sequence of nitrogenous bases in DNA determines the order of amino acids, thus dictating the protein. The genetic code is written in a language that only has four letters: A,U,G &C! These letters (nucleotides) combine in different ways to form the code for twenty different amino acids. The genetic code is read three letters (nucleotides) at a time in groups called codons. 64 possible codons (4 bases3) …some amino acids can be coded for by more than one codon… …can you give an example? One codon, AUG, can specify methionine or “start” codon for protein synthesis. Note the three “stop” codons that do note code for any amino acid – they signal the end of a polypeptide chain. Consider the following mRNA sequence: U C G C A C G G U This sequence would be read three bases at a time as: UCG - CAC -GGU The codons represent different amino acids: UCG - CAC -GGU (Serine - Histidine – Glycine) Translation mRNA leaves the nucleus, attaches to ribosome… …in the ribosome, the amino acid is transferred to the growing polypeptide chain. …starting at AUG, mRNA’s codon attracts tRNA ‘s anticodon with its amino acid… Transcription AND Translation! Videos for Review • Replication http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/DNAReplicationBasic_w_FX.html • Transcription http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/TranscriptionBasic_withFX.html • Translation http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/TranslationBasic_withFX0.html