* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Term1 Cell Analogy Portfolio Product
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
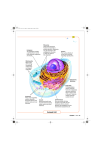
Name: Eukaryotic Cell Analogy Project Planning Organizer Project Purpose: To demonstrate your understanding of the parts of the eukaryotic cell, their functions and the ways they work together to sustain the cell’s life processes. MA Cell Biology Standards: 2.1 Relate cell parts/organelles (plasma membrane, nuclear envelope, nucleus, nucleolus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, ribosome, vacuole, cell wall, chloroplast, cytoskeleton, centriole, cilium, flagellum, pseudopod) to their functions. Components: the components of your project must be as follows: 1. a 2- or 3-dimensional model of your analogy, made with materials of your choosing that you must obtain yourself. You may build a physical model, draw by hand, or create a computer model or presentation. 2. 8 labels that adequately introduce each part of your analogy, its function within your analogy, and how it compares to a part of the eukaryotic cell. The language you use between the two parts of your label should be parallel (see example below). Your labels should follow the following general format: For example, if your analogy were of the cell as a restaurant: Did you notice the use of parallel language in this example? Here are some steps to get you started: 1) Use your Big Black Biology Book and any other resources to look up the functions of each of the cell parts. Write the definition and the role or function of each part. (PART and FUNCTION) 2) Once you have researched all of the cell part, decide what other objects or system has parts that are similar to cell parts. Is the cell like a car? A house? A factory? A restaurant? A school? 3) Choose your analogy (what you will compare to a cell). 4) Fill in the right side of the organizer with the PART and the FUNCTION of your comparison/analogy. 5) You may email [email protected] to see sample projects. Scoring Guide Here are the organelles that you must include in your project and make your labels for ( 5 points each ): A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Part Analogy (example) Nucleus : boss, manager, director, etc. Cell Membrane : wall, gate, fence, etc. Rough endoplasmic reticulum ( rough ER ): work area with the workers (ribosomes) Ribosomes : workers, employees, etc. Golgi apparatus (or Golgi complex): place for modifying, inspecting, packing, shipping product Mitochondria : energy source Vacuole : storage or waste area (for water reserves or trash) Protein : what you are making or producing. Here are organelles that you can include for extra credit (1 point each): I. Vesicles : packages/boxes to transport products in, around, and out of the building. J. Chloroplast : converts sun energy to food K. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum ( smooth ER ): produces factory parts, breaks down toxic substances L. Cytoskeleton/cytoplasm : provides structure and storage space for building. M. Lysosome : worker who cleans up trash and waste in building. N. Nuclear Envelope : walls of boss’ or manager’s office O. Nuclear pore : door to boss’ or manager’s office P. Nucleolus : hiring or training office; where workers are made. Grading : Your project will be graded according to the following criteria (46 points) Creativity, artistic merit, and overall fitness of your analogy : 10 points Labels : 4 points each, 32 points total A. Nucleus: 1 2 3 4 B. Cell Membrane: 1 2 3 4 C. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER): 1 2 3 4 D. Ribosomes: 1 2 3 4 E. Golgi apparatus: 1 2 3 4 F. Mitochondria: 1 2 3 4 G. Vacuole: 1 2 3 4 H. Protein: 1 2 3 4 I. Optional bonus points a. Other: b. Other: c. Other: d. Other: e. Other: f. Other: g. Other: h. Other: Neatness and legibility : 4 points 1 2 3 4 Here are the organelles that you must include in your project and make your labels for ( 5 points each ): DO CELL SIDE FIRST CELL part Nucleus DO THIS SIDE LAST FUNCTION of part ANALOGY part FUNCTION of part Cell membrane Rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes Golgi apparatus Mitochondria Vacuole Protein A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. Nucleus : boss, manager, director, etc. Cell Membrane : wall, gate, fence, etc. Rough endoplasmic reticulum ( rough ER ): work area with the workers (ribosomes) Ribosomes : workers, employees, etc. Golgi apparatus (or Golgi complex): place for modifying, inspecting, packing, shipping product Mitochondria : energy source Vacuole : storage or waste area (for water reserves or trash) Protein : what you are making or producing. Here are the organelles that you may include for extra credit ( 1 point each ): DO CELL SIDE FIRST CELL part Vesicles DO THIS SIDE LAST FUNCTION of part ANALOGY part FUNCTION of part Chloroplast Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Cytoskeleton/cytoplasm Lysosome Nuclear envelope Nuclear pore Nucleolus Cell Biology Performance Indicators Rubric - DESE Needs Improvement Proficient Advanced Identifies most cell Describes the functions of Describes the makeup of a parts/organelles and organelles within the cell cell membrane and explains describes some of their and describes various forms its role as a highly selective functions of cell membrane transport barrier As you can see, to reach the level of Proficient or Advanced, you will have to go beyond describing the parts and their functions, and explain transport across the cell membrane.