* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
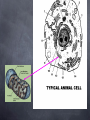
Download The Cell Organelles (Typical Animal Cell) Cell Organelles are small
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
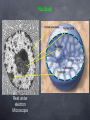
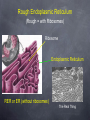
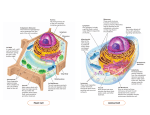
The Cell Organelles (Typical Animal Cell) Cell Organelles are small structures that help carry out life functions Cell Membrane Nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes Golgi Body Lysosome Mitochondria Vacuoles Cell Membrane The cell membrane separates the cell from its surrounding environment, The membrane controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell. This makes it possible for the cell contents to be chemically different from the environment. It is described as “selectively” or “semi” permeable because not all things can go through See image next page Lipid Bilayer Enzyme Protein Receptor Protein Channel Nucleus The control center for metabolism and reproduction. Houses the genetic information (chromosomes). See image next page Nucleus Real under electron Microscope Endoplasmic Reticulum System of fluid-filled canals, or channels, enclosed by membranes. Serve as paths to transfer materials throughout the cell. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough = with Ribosomes) Ribosome Endoplasmic Reticulum RER or ER (without ribosomes) The Real Thing Ribosomes The site of protein synthesis. These Ribosomes are colored enhanced. They can be found on the ER or floating in the cytoplasm Golgi bodies Golgi bodies aid in the preparation and storage of molecules to be secreted by the cell. Proteins made at ribosomes are often packaged by the Golgi complex R.ER These two organelles often work together Golgi body Golgi In Action Outside Cell Inside Cell Lysosomes Involved in the digestion of food with in the cell. They contain enzymes - they will eventually combine with food vacuoles to digest food. Sometimes they are opened up and destroy worn-out cells Mitochondria Releases energy stored in food molecules (cellular respiration). Food = chemical bond energy = organic molecule Cellular Respiration Taking energy out of food and converting it into a form that can be used by the cell (ATP) Vacuole Storage site for cell products (water, food, waste products) Plant Cell Cell Wall Lies just outside the cell membrane, and gives the cell its shape and provides protection for the cell. (Adds Structural Support) Mainly made of the carbohydrate called cellulose Large Vacuole Plant cells have large vacuoles that are typically used as a storage site for waste products. Very Large Chloroplast The place where photosynthesis takes place. They are green because they contain a green pigment called chlorophyll The green pigment captures the light energy The End