* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Cell - Effingham County Schools
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
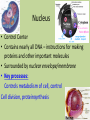
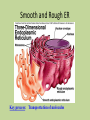
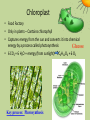
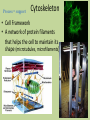
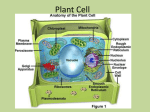
Plant Cell Nucleus • Control Center • Contains nearly all DNA – instructions for making proteins and other important molecules • Surrounded by nuclear envelope/membrane • Key processes: Controls metabolism of cell, control Cell division, proteinsynthesis Chromosome • (The Data) … all the directions • (DNA) Nucleolus • Nucleolus – small dense region inside nucleus. Ribosomes are made here. Endoplasmic Reticulum • Transportation • Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) – Covered in ribosomes (rough) – Makes and transports proteins, especially membrane proteins • Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) – Synthesis (make) of membrane lipids – Contain enzymes that can detoxify drugs – Liver has lots of SER’s Notice how the E.R. is attached to the nucleus …. Like the ‘hallways’ Smooth and Rough ER Key process: Transportation of molecules Ribosomes! • Protein Factory • Proteins are assembled on these organelles by following coded instructions from the nucleus Key process: Proteinsynthesis Golgi Apparatus • Packaging Center • Modify, sort, and package proteins and other materials from the endoplasmic reticulum for storage or secretion. Key processes: Packaging and sorting of proteins http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/ve siclebudding.html http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp04/0402002.ht ml Mitochondria • Power House • Convert chemical energy stored in food to a form a cell can use (ATP) during the process of cellular respiration. • Contain own ‘Mitochondrial DNA’ • Has double membrane Key process: Cellular respiration C6H12O6 + O2 H2O +CO2 + ATP Glucose Oxygen Water Carbon dioxide Energy Chloroplast • Food Factory • Only in plants – Contains chlorophyll • Captures energy from the sun and converts it into chemical energy by a process called photosynthesis Glucose • 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy (from sunlight) C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Key process: Photosynthesis Plastids - Chloroplasts, Chromoplasts and Leucoplasts • Chromoplasts contain pigments that give flowers, fruit and autumn leaves their orange, yellow and red colors. •Leucoplasts store starch and other molecules for the cell. Many in potato cells. Process - Storage Mitochondria/Chloroplasts • These two utilize energy from food and the sun respectively and convert it into energy the cell can use. Process = support Cytoskeleton • Cell Framework • A network of protein filaments that helps the cell to maintain its shape (microtubules, microfilaments) • Storage Facility Vacuoles • Plants have big vacuoles • Store materials like water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates • In plants, there is a large vacuole which helps with maintaining pressure (turgor pressure) Support Process – Storage and Support Cell boundaries aka cell membrane • Cell membrane regulates what enters/leaves the cell. Process - Osmosis Process = Support and protection • • • • Cell Wall Castle Wall Only in Plant Cells Provides support and protection for cell Mostly made of cellulose – Cellulose is the key component of wood and paper Cytoplasm Key process = Metabolism – all the chemical reactions that take place in the cell. Jelly like substance that contains the organelles.