* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Q4 Describe the factors that affect the flux of
Survey
Document related concepts
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
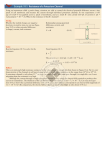
Q4 Describe the factors that affect the flux of potassium across the cell membrane (March 2012) Potassium § § § Total amount of potassium in the body 40-‐45 mmol/kg. Major intracellular cation (ICF concentration 150mmol/L, extracellular concentration 3.5-‐5mmol/L) Distribution of K is ICF = 90%, ECF = 2% and Bone = 8%. Functions of potassium § § § § Maintenance of the resting membrane potential and generation of action potentials Intracellular tonicity and pH regulation DNA and protein synthesis Growth and enzyme function Factors affecting potassium flux across the membrane: § § § § § § § § Plasma K levels à as per Fick’s Law of Diffusion, the diffusion of a substance across a semipermeable membrane is directly proportional to the concentration gradient across the membrane. Temperature à temperature affects the calculation of the Nernst equation Aldosterone à upregulates Na/K ATPase to increase K uptake into cell Insulin à upregulates the Na/K ATPase pump Adrenaline à upregulates Na/K ATPase, mediated by beta2 receptor activation Acid base status à in acidaemia, upregulation of the K/H+ antiporter occurs (pumping H+ into cell and K+ out of cell). Reduced activity of the Na/K ATPase may also occur Osmolality à cellular dehydration causes a relative increases in intracellular K concentration, promoting diffusion out of the cells Exercise à will decrease pH levels hence increasing plasma K Judith Askew 2014