* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL CYCLE
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
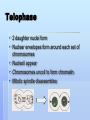
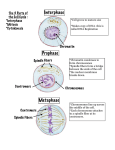
CELL CYCLE Mitosis DNA In order for the DNA to fit inside the nucleus, it must compact itself by coiling When DNA is unwound it is called chromatin When the DNA is completely compacted it is in the form of chromosomes Cell Cycle Period from the beginning of one cell division to the beginning of the next cell division Divided into 2 parts: Interphase Cell Division Interphase Occurs between cell divisions Cell prepares all the materials necessary for cell growth and prepares it for division Accounts for 90% of the total time in the cell cycle Divided into 3 stages: G1 S G2 G1 Also known as gap 1 Characterized by growth and development S Also known as the synthesis phase Once the cell enters the S phase it is committed to cell division Chromosomes in the nucleus replicate G2 Also known as gap 2 Cell makes organelles and other materials Centrioles replicate to form 2 pairs Cell Division Splitting of one cell to form 2 cells Divided into 2 parts: Mitosis Cytokinesis Mitosis Process during which a cell’s nucleus divides into two identical nuclei It is divided into 4 phases: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Prophase Nucleus condenses Proteins form microtubules which form a fibrous structure called the mitotic spindle Spindle stretches out between opposite poles of the cell Nuclear envelope and nucleolus break down Centromere attaches to spindle fibers Fibers move chromatids to center of cell Metaphase Chromosomes are pulled to center of cell Chromosomes line up on an imaginary line called the metaphase plate ALIGNMENT IS CRUCIAL TO ENSURE THAT EACH CELL GETS A COMPLETE SET OF CHROMOSOMES Anaphase Centromeres divide Spindle fibers pull chromatids toward opposite poles Chromatids are 2 identical sets of daughter chromosomes Ends when chromosomes are at opposite ends of the cell Telophase 2 daughter nuclei form Nuclear envelopes form around each set of chromosomes Nucleoli appear Chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin Mitotic spindle disassembles Cytokinesis Process in which the cell’s cytoplasm divides to make 2 daughter cells Each daughter forms around 1 of the 2 nuclei produced during mitosis Steps in Cytokinesis Begins during telophase The cell membrane, at the center of the cell, folds inward to form a cleavage furrow The cell continues to pinch in half at the furrow until the membrane meets and forms a division resulting in 2 cells with complete cell membranes