* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
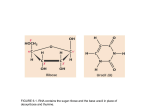
BIOL. 303 EXAM III 4/19/07 Name_____________________________ ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------This exam consists of 40 multiple choice questions worth 2.5 points each. On the separate testing form, please fill-in the single best choice for each question. Be sure to fill-out your student number and name on the answer sheet. Good luck! ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. In 1964, Nirenberg and Leder used the triplet binding assay to determine specific codon assignments. A complex of which of the following components was trapped on the nitrocellulose filter? 1. 2. 3. 4. 2. ribosomes and DNA charged tRNA, RNA triplet, and ribosome free tRNAs uncharged tRNAs and ribosomes. AUG is almost always the: 1. intron 2. exon 3. anticodon 4. initiation codon 3. Peptidyl transferase is associated with the action of the: 1. ribosome 2. template strand 3. nucleus 4. cytoplasm 4. Transcribed regions present in the mature mRNA would arise from a(n) ________, while transcribed regions NOT present in the mature mRNA would arise from a(n) ________. 1. 2. 3. 4. intron; exon exon; intron codon; anticodon anticodon; codon 5. Ribosomes are composed of: 1. tRNA and protein 2. mRNA and protein 3. rRNA and protein 4. proteins only 6. Which of the following is not true of tRNA? 1. it contains modified bases 2. it contains thymine 3. it has secondary structure 4. it has anticodon loop 7. A defect in aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase would directly lead to: 1. a block in transcription 2. uncharged tRNA 3. 1 & 2 4. none of the above 8. What property of the genetic code allows the use of several codons for a particular amino acid? 1. near universality 2. degeneracy 3. non-overlapping codons 4. reading frame 9. By their experimentation using auxotroph mutants of the Neurospora fungus, Beadle and Tatum were able to propose the hypothesis that: 1. prototrophs will grow only if provided with nutritional supplements. 2. several different enzymes may be involved in the same step in a biochemical pathway. 3. the role of a specific gene is to produce a specific enzyme. 4. more than one codon can specify a given amino acid. 10. Consider the pathway shown below for the synthesis of the amino acid arginine in Neurospora. ARG-F, G, and H are the names of the genes controlling the steps of the pathway: ornithine ARG-F → citrulline ARG-G → ARG-H succinate → arginine Mutant strains of Neurospora are grown in minimal media with supplements as follows. Each mutant strain carries only a single mutation. Growth is shown by (+), no growth is shown by (0): mutant strain a b c nothing 0 0 0 ___ ornithine 0 0 0 Supplements__________________ citrulline succinate arginine 0 0 + 0 + + + + + Which is statement is correct? 1. strain a is defective in ARG-G 2. strain a is defective in ARG-F 3. strain b is defective in ARG-G 4. strain c is defective in ARG-H 11. In the lac operon, under which of the following conditions will the lac genes be transcribed at high levels? 1. 2. 3. 4. 12. low glucose, low lactose high glucose, low lactose low glucose, high lactose high glucose, high lactose RNA polymerase binds to the: 1. 2. 3. 4. operator promoter repressor inducer 13. For the E. coli genotype I+P+OcZ+Y+A+, the expression of β-galactosidase will be: 1. inducible 2. constitutive 3. absent 4. none of the above 14. The lac operon 1. is under negative and positive control. 2. is under positive control only. 3. is normally expressed constitutively. 4. is an example of tissue-specific expression. 15. With regards to the trp operon, 1. tryptophan is an inducer. 2. tryptophan is a co-repressor. 3. attenuation can halt replication. 4. none of the above. 16. Under the system of genetic control of the trp operon, 1. when there are high levels of tryptophan in the medium, transcription of the trp operon occurs at high levels. 2. when there is no tryptophan in the medium, transcription of the trp operon occurs at high levels. 3. when there are high levels of tryptophan in the medium, transcription of CAP occurs at high levels. 4. when there are high levels of tryptophan in the medium, ribosomes “stall” and reduce the levels of tryptophan synthesized. 17. Regarding the trp operon in B. subtilis, TRAP influences gene expression 1. 2. 3. 4. at the transcriptional level. at the translational level. both 1 and 2 none of the above 18. In the absence of arabinose, the AraC protein induces a regulatory secondary structure in _________. 1. protein 2. DNA 3. mRNA 4. arabinose 19. Three posttranscriptional modifications often seen in the maturation of mRNA in eukaryotes are 1. 2. 3. 4. 20. 5'-capping, 3'-poly(A) tail addition, splicing 3'-capping, 5'-poly(A) tail addition, splicing removal of exons, insertion of introns, capping 5'-poly(A) tail addition, insertion of introns, capping Protein-encoding genes in eukaryotes are transcribed by 1. RNA polymerase I 2. RNA polymerase II 3. RNA polymerase III 4. RNA polymerase IV 21. Transcription factors act as_________. 1. cis-acting regulatory elements 2. trans-acting regulatory elements 3. promoters 4. enhancers 22. SWI-SNF proteins are involved in: 1. 2. 3. 4. basal transcription RNA interference repression chromatin remodeling 23. Eukaryotic cells are able to carefully regulate precise levels of transcription in specific genes encoding structural proteins through: 1. complex enhancer elements that can associate with multiple activator and repressor proteins 2. production of different types of sigma factors 3. attenuation 4. all of the above 24. Which of the following methods of regulation is not present in prokaryotes? 1. 2. 3. 4. DNA-binding proteins attenuation repressor proteins chromatin remodeling 25. What modification neutralizes the charges on histones and loosens up the interactions between histones and DNA? 1. phosphorylation 2. methylation 3. acetylation 4. polyadenylation 26. Which of the following can account for multiple proteins from a primary transcript? 1. alternative splicing 2. reverse transcription 3. 5' methylation 4. polyribosomes 27. The term "chromatin remodeling" refers to 1. alteration of chromatin structure in association with transcription. 2. a process that only bacteria perform since they contain no nucleus. 3. a process that is exclusively associated with transcription by RNA polymerase III in eukaryotes. 4. alteration in chromatin structure to facilitate loading and translation by ribosomes and, thus, enhance gene expression. 28. The phenomenon known as “RNAi” (RNA interference) can be used experimentally to 1. 2. 3. 4. reduce expression of a specific target gene. reduce transcription rate from a specific gene promoter. interfere with replication. enhance gene expression. 29. Controls that tie the integrity of the genome with progression through cell division are known as: 1. growth factors 2. receptors 3. cyclins 4. checkpoints 30. Colonization of distal sites by cancer cells is known as: 1. metastasis 2. angiogenesis 3. clonal replication 4. apoptosis 31. Wild-type genes that can cause cancer through increased expression are: 1. tumor suppressor genes 2. proto-oncogenes 3. CDK inhibitors 4. nonexistent 32. Wild-type genes that can cause cancer through a loss-of-function mutation are: 1. 2. 3. 4. tumor suppressor genes oncogenes proto-oncogenes cyclin-dependent kinases 33. Sporadic cancer arises from __________; familial cancer arises from _________. 1. somatic mutations; germline mutations 2. somatic mutations; germline and somatic mutations 3 .germline mutations; somatic mutations 4. germline mutations; stem cell mutations 34. What is the name of the protein that helps to regulate multiple checkpoints throughout the cell cycle and is also known as the “guardian of the genome?” 1. p34 2. p102 3. cyclin 4. p53 35. A person born with an inherited predisposition to cancer usually does not develop cancer until after 1. 2. 3. 4. exposure to radiation. LOH of the inherited mutation. age 70 Mardis Gras 36. Regarding the relationship between viruses and cancer, which statement is most accurate? 1. viruses cause some cancers in animals, but viruses are not associated with cancer in humans. 2. most human cancers are known to be caused by viruses. 3. viruses are not associated with cancer in animals or humans 4. some human cancers are closely associated with viral infection and some cancers can possibly be prevented by vaccination against virus. 37. What is the function of an antibiotic-resistance gene in a vector? 1. To allow resistant transformants to grow in selective medium 2. To distinguish introns from exons 3. To screen for vectors with inserts 4. To allow plasmid replication 38. What information is present in a cDNA library? 1. 2. 3. 4. 39. intron sequences promoter sequences exon sequences telomere sequences What is the function of dideoxynucleotides in Sanger DNA sequencing? 1. They act as primers for DNA polymerase. 2. They act as primers for reverse transcriptase. 3. They cut the sequenced DNA at specific sites. 4. They stop synthesis at a specific site, so the base at that site can be determined. 40. Which of the following is needed in order to amplify a DNA fragment by PCR? 1. a set of primers. 2. knowledge of the complete nucleotide sequence of the fragment to be amplified. 3. RNA polymerase. 4. dideoxynucleotide triphosphates. That’s all! ITEM NUMBER 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 CORRECT ANSWER 2 4 1 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 3 2 2 1 2 2 3 2 1 2 2 4 1 4 3 1 1 1 4 1 2 1 2 4 2 4 1 3 4 1