* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transgenic plant Herbicide Resistance
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
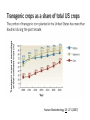
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
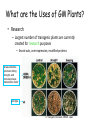
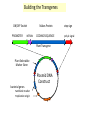
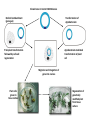
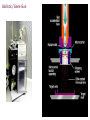
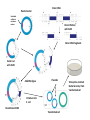
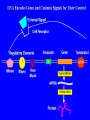
Plant Genetic Engineering (Plant Transformation) Nono Carsono, PhD. Dr. rer. nat Suseno Amien Anas, PhD. Genetic transformation/modification of plant? • Introduction of exogenous DNA into a plant cell - transient: no incorporation of exogenous DNA (transgenes) into the genome - stable: incorporation into genome Transgene - the genetically engineered gene added to a (plant) species Stable expression of GFP Product - Transgenic plant: plant containing transgenes introduced by genetic engineering/modification/ transformation (not classical breeding) • Transformation of multicellular organisms: - can not directly transform every cell transformation involves one cell which then regenerates an entire organism Transient expression of GFP Why use Genetic Transformation? • Accelerate the breeding process – Introduce/enhance desired trait in an established genetic background • Extend the gene pool – Select genes from any Kingdom (with care, especially if potential for entry into the food chain) Diff. between conv. breeding and genetic engineering Parameter Conventional Breeding Genetic engineering Level Whole plant Cell/organelle Precise Many genes One gene or some Taxonomy barrier Within species/genus No restriction Certainty Genetic change- hard Genetic change to estimate quite easy to estimate Bt Corn Reduces: Insecticide Mycotoxin Application Production What are the Uses of GM Plants? • Research – Largest number of transgenic plants are currently created for research purposes • Knock-outs, over-expression, modified proteins stress-inducible promoter driving drought- and cold-responsive transcription factor wild type K. Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, JIRCAS, Japan What are uses of GM Plants? • Commercial Applications – Altered agronomic traits time • • • • • • Disease/insect resistance Virus resistance Herbicide resistance Salt/drought tolerance Cold tolerance 2007 Enhanced yields, other quantitative traits • Phytoremediation • Production of vaccine Application of Roundup herbicide Field following application Other uses of GM Plants? • Bioreactors / Molecular farming – Therapeutic proteins • Human lactoferrin to treat iron deficiencies • Antibodies – Vaccine production • Antigen expression – HepC, HIV Dow AgroSciences Achieves World’s First Registration for Plant-Made Vaccines Indianapolis, IN - January 31, 2006 Dow AgroSciences LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of The Dow Chemical Company, (NYSE: DOW), announced today that it has received the world's first regulatory approval for a plant-made vaccine from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Center for Veterinary Biologics. This approval represents an innovative milestone for the company and the industry... Other uses of GM Plants? • Functional foods (humans and livestock) – Today: Golden rice • Vitamin A enriched – Future directions: • Boosted antioxidants • Elevated content of specific minerals • Removal of food allergens, carcinogens Greater public acceptance when the technology is shown to more greatly benefit consumers? Golden Rice Scientists from Swiss and German universities have engineered two genes from daffodil and one bacterial gene into rice to produce provitamin A. Provitamin A biosynthesis pathway GGPP Phytoene synthase (psy) Phytoene (daffodil) Phytoene desaturase (crtl) Lycopene (bacteria) Funding: Rockefeller Foundation, Swiss Federal Institute Of Technology, European Community Biotech Program Lycopene ß-cyclase (lcy) beta-Carotene = provitamin A (daffodil) An Overview of the Genetic Engineering/modification cycle Prerequisites for genetic transformation • Available gene of interest (incl. selectable marker and other regulatory sequences)- isolation and construct design • Efficient method for genetic transformation- gene transfer • Efficient method for regeneration (whole plant)- plant regeneration ? Promoter Bt coding sequence Termination sequence How the direction of transcription? Right or left? Building the Transgenes ON/OFF Switch PROMOTER INTRON Makes Protein CODING SEQUENCE Plant Transgene Plant Selectable Marker Gene Plasmid DNA Construct bacterial genes •antibiotic marker •replication origin stop sign poly A signal Transformation Cassettes Contains 1. Gene of interest • The coding region and its controlling elements 2. Selectable marker • Distinguishes transformed/untransformed plants 3. Insertion sequences • Aids Agrobacterium insertion Transformation Steps Prepare tissue for transformation • Tissue must be capable of developing into normal plants • Leaf, germinating seed, immature embryos Introduce DNA • Agrobacterium or gene gun Culture plant tissue • Develop shoots • Root the shoots Field test the plants • Multiple sites, multiple years Delivering the gene to the plant genome: Gene transfer methods • Direct transfer of DNA - PEG-polyethylene glycol - Electrophoration • Transfer of DNA via carrier - Microinjection - Particle bombardment • Transfer of DNA via vector - Agrobacterium tumefaciens - Viral vector Cloned Gene in Vector DNA Molecule Biolistic bombardment (gene gun) Transformation of Agrobacterium Protoplast transformation followed by cell wall regeneration Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of plant cell Migration and integration of gene into nucleus Plant cells grown in tissue culture Regeneration of genetically modified plant from tissue culture Biolistic / Gene Gun Plasmid vector Donor DNA Selectable antibiotic resistance marker Donor DNA cut with EcoRI Donor DNA fragments Vector cut with EcoRI Add DNA ligase Plasmids Introduce into E. coli Recombinant DNA Transformed cell Tetracycline-resistant Bacterial colony from transformed cell The Next Test Is The Field Herbicide Resistance Non-transgenics Transgenic plant Example: Final Test of the Transgenic Consumer Acceptance RoundUp Ready Corn Before After Roadmap Bioengineering Plants for the Future Plant production platforms Health food and quality - Amino acids - Oil - Starch Efficient agriculture - Bt technology - Herbicide resistance etc 1997 2005 Plant protection - Viruses Nematodes Fungi Insects 2015 - Vitamines Fatty acids Enzymes Bio-polymers Pigments Pharmaceutical products Fibers Stress resistance - Cold - Drought - Salinization 2025 Nature Biotechnology 25: 271 (2007) Nature Biotechnology 25: 271 (2007) Nature Biotechnology 25: 271 (2007) Transgenic Confirmation (Genotypic analysis) PCR for rapid screening Southern blot for precise gene detection Northern blot for transcription analysis Western blot for translation analysis, together with Ab-binding or enzymatic analysis • Mendelian analysis for insertion locus and linkage analysis • In situ hybridization for precise insertion locus analysis • DNA methylation analysis for silencing potential analysis • • • • Regulatory principles of transgenic crops: 1. Scientifically based, based on information of organism, used technology and effects to humans and environment 2. Product-based approach, use existing product-based legislation 3. Familiarity and substantial equivalence, experience with the use of that species. The determination is based on scientific literature and practical experience with the plant and similar plant varieties. 4. Case-by case, allow the development of knowledge that could inform criteria and requirement over time. Regulatory principles: 5. 6. 7. 8. Step-wise fashion, products should be assessed throughout the chain of development : From laboratory to greenhouse and finally large-scale field trial Transparency Precautionary principle/approach, derived from Rio Declaration, regulatory groups can make decisions about products based on scientific uncertainty. Harmonization, sharing of or acceptance of another group’s review Questions Do not forget..next week student presentation!