* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint Presentation - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA methylation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetyltransferase wikipedia , lookup
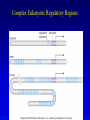
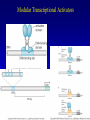
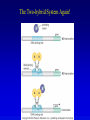
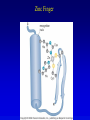
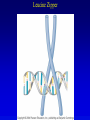
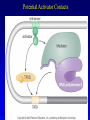
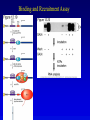
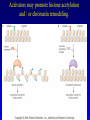
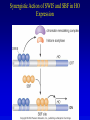
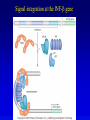
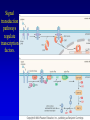
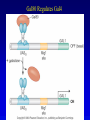
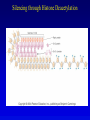
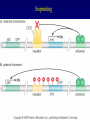
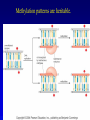
Chapter 17 Regulation in Eukaryotes 1 and 3 November, 2006 • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Overview Transcriptional initiation is the most common point to regulate gene expression. Eukaryotes must also integrate more signals, and must modify nucleosome positioning in order to activate transcription. Eukaryotic transcriptional activators are often modular, with DNA binding and activation domains. Eukaryotic transcriptional activators may bind as heterodimers. Classes of eukaryotic transcriptional activators include homeodomain, zinc finger, leucine zipper, and helix-loop-helix. Activators recruit the transcriptional machinery to the gene, interacting with mediator or TFII general factors. Activators may also promote chromatin modification. Insulators block activation by enhancers. Locus control regions open up chromatin to regulation by activators. Activators act synergistically. Eukaryotic transcription may be repressed by blocking or binding activators, interacting with mediator, or by modifying chromatin. Signal transduction pathways communicate with transcriptional regulators. DNA and histone modification can collaborate to effect regulation. Regulation may also occur at the levels of splicing, translation, and RNA stability. Complex Eukaryotic Regulatory Regions Modular Transcriptional Activators The Two-hybrid System Again! Homeodomain Zinc Finger Leucine Zipper Helix-Loop-Helix Potential Activator Contacts Activator Bypass by LexA-Mediator Fusion ChIP can identify binding sites. Binding and Recruitment Assay Gal4 recruits TFIIB Activators may promote histone acetylation and / or chromatin remodeling. Insulators block the effects of activators at enhancers. Locus control regions make clusters of genes available for activation. Possible Modes of Cooperative Binding of Activators Synergistic Action of SWI5 and SBF in HO Expression Signal integration at the INF-b gene Combinatorial Control Control of Cell-type Specific Genes in Yeast Possible Modes of Action for Eukaryotic Repressors. Signal transduction pathways regulate transcription factors. Gal80 Regulates Gal4 Silencing through Histone Deacetylation Silencing sometimes involves methylation and histone deacetylation. Imprinting Methylation patterns are heritable. Transcriptional Regulation of Sxl Regulated Alternative Splicing Translational Control of GCN4 RNAi Cooperative and Non-Cooperative Binding Title Title