* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Typical” Animal Cell “
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
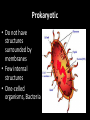
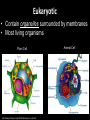
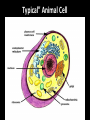
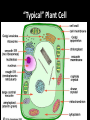
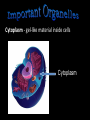
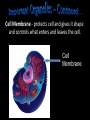
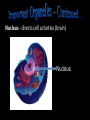
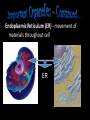
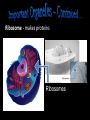
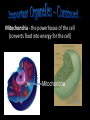
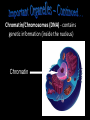
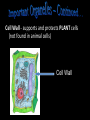
The Cell Theory • The cell is the basic unit of structure and function (a.k.a. – life) • All living things are made up of 1 or more cells • Cells come from other, preexisting cells (a.k.a. – reproduction) Scientists Involved in the Cell Theory 1. Hooke • 1st person to describe cells. Built microscope in 1665. 2. Van Leeuwenhoek • Discovered the diversity of cells 1673. 3. Schleiden and Schwann (1838-1839) • All organisms are made of one or more cells. • The cell is the basic unit of all living things. 4. Later (1858) Virchow added • All cells come from existing cells. What is a cell? • It is the smallest unit of life that carries out life functions Animal Cell Plant Cell Two Types of Cells •Prokaryotic •Eukaryotic Prokaryotic • Do not have structures surrounded by membranes • Few internal structures • One-celled organisms, Bacteria Eukaryotic • Contain organelles surrounded by membranes • Most living organisms Plant Cell http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html Animal Cell Typical” Animal Cell “Typical” Plant Cell What’s Inside? • Organelles – tiny structures within a cell that perform specific jobs to keep the cell alive Cytoplasm - gel-like material inside cells Cytoplasm Cell Membrane - protects cell and gives it shape and controls what enters and leaves the cell. Cell Membrane Nucleus - directs cell activities (brain) Nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) - movement of materials throughout cell ER Ribosome - makes proteins Ribosomes Mitochondria - the powerhouse of the cell (converts food into energy for the cell) Mitochondria Chromatin/Chromosomes (DNA) - contains genetic information (inside the nucleus) Chromatin Chloroplast - takes energy from the sun and makes food for the PLANT cell (not found in Animal Cells) Chloroplast Cell Wall - supports and protects PLANT cells (not found in animal cells) Cell Wall Vacuole - storage of food and water Vacuole Golgi Body - packages and moves proteins Golgi Body Lysosome - digests wastes Lysosome