* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RNA Ribonucleic Acid - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
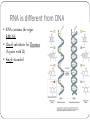
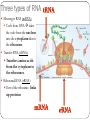
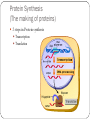
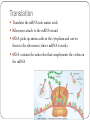
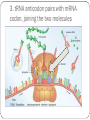
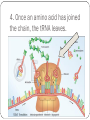
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) How is RNA different from DNA? Lets Review DNA What sugar does it have? Adenine pairs with ___________ Cytosine pairs with __________ Double or single stranded? RNA is different from DNA RNA contains the sugar RIBOSE Uracil substitute for Thymine (A pairs with U) Single stranded DNA TO RNA DNA=ATTGCAC RNA=UAACGUG RNA? Who cares? Why is RNA important? It contains the code from DNA that is needed to make proteins! Three types of RNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) Code from DNA takes the code from the nucleus into the cytoplasm then to the ribosome. Transfer RNA (tRNA) Transfers amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Part of the ribosome, links up proteins Protein Synthesis (The making of proteins) 2 steps in Protein synthesis Transcription Translation Transcription mRNA copies the code from DNA, and travels through cytoplasm to ribosome where it sticks. Let’s Do Transcription! DNA= A G CT GA mRNA= U C G A C U Codons Three nitrogen bases. Codons code for the genetic code! Each amino acid is coded for by 3 mRNA bases If you string a bunch of amino acids together, what do you get?? 1 CODON = 1 AMINO ACID = 3 NUCLEOTIDES Translation Translates the mRNA into amino acids. Ribosomes attach to the mRNA strand tRNA picks up amino acids in the cytoplasm and carries them to the ribosomes (where mRNA is stuck). tRNA contains the anticodon that complements the codon on the mRNA Translation: The Details What are codons again?? 1. mRNA strand leaves the nucleus, enters cytoplasm, attaches to ribosome. 2. tRNA molecules pick up amino acids in cytoplam and carries them to ribosomes 3. tRNA anticodon pairs with mRNA codon, joining the two molecules 4. Once an amino acid has joined the chain, the tRNA leaves. 5. The process continues until a chain of amino acids is formed and stops once a stop codon on the mRNA is reached. Translation DNA =A T G C T A mRNA = U A C G A U (Codon) tRNA = A U G C U A (Anticodon) TRANSCRIPTION Takes place in the nucleus translation Moves out of nucleus into the cytoplasm & attach to ribosome Steps to figure out the genetic code 1. Obtain a DNA Template. (a row of DNA bases) 2. Transcribe DNA into mRNA 3. Use the codons (mRNA) to translate into amino acids let’s practice! DNA TAC mRNA (Codon) AUG tRNA Strand (anticodon) UAC Amino Acids Start More practice needed? DNA= TAC -GAT-GCC-ATC mRNA= AUG -CUA- CGG-UAG tRNA= UAC -GAU-GCC-AUC Amino Acids= START-LEU-ARG-STOP MUTATIONS Change in the genetic code May occur in the genes or the chromosomes ONLY MUTATIONS IN GAMETES MAY BE PASSED TO OFFSPRING. Two types: Point Frameshift Point Mutations (in the genes) Only change a few nucleotides Examples: Substitution – one base is changed to another Insertion – a base is added to the gene Deletion – a base is removed from the gene Frame-shift Mutations (in the genes) Change the reading frame Examples: Chromosomal Mutations Change the number or structure of the chromosomes Examples: Deletion – losing all or part of the chromosome Duplication – extra copies of parts of the chromosome Inversion – reversing the order of the pieces of the chromosome Translocation – pieces of chromosomes break off and stick to another chromosome Significance of Mutation Some mutations are neutral – not good, not bad. Mutations that change the specific proteins needed are usually harmful Some mutations are good! Like those of your who now can digest lactose.