* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BN21 subcortical motor control
Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Perivascular space wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Substantia nigra wikipedia , lookup
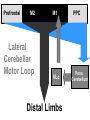
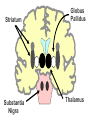
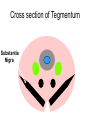
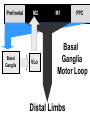
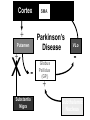
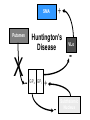
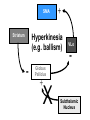
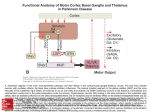
Subcortical Motor Systems: Cerebellum & Basal Ganglia Lecture 21 Motor Loops Cortex Subcortex Cortex Spinal cord Cerebellum coordination of movement Basal Ganglia selection & initiation of voluntary movements ~ Cerebellum Nonmotor functions - memory/language Coordination of complex movements Programs ballistic movements no feedback during execution direction, force, & timing Motor learning shift from conscious unconscious ~ Cerebellum: Anatomy Folia & lobules analogous to sulci & gyri Vermis - along midline output ventromedial pathway Hemispheres output lateral pathway Deep cerebellar nuclei analogous to thalamus ~ Motor Loop Through Cerebellum Lateral cerebellum simplest circuit 20 million axons Cortex pons & cerebellum Prefrontal, Motor, PPC Pons & Cerebellum thalamus VLc - ventrolateral nucleus VLc M1 lateral pathway ~ Prefrontal M2 Lateral Cerebellar Motor Loop M1 VLc Distal Limbs PPC Pons, Cerebellum Cerebellum: Damage Lesions - loss of motor coordination Dysynergia no simultaneous movement of joints serial movement only Dysmetric movements to wrong coordinates Alcohol intoxiction depression of cerebellar circuits ~ Basal Ganglia Caudate nucleus Putamen Globus Pallidus Striatum Substantia Nigra Tegmentum Control slow movements Using immediate sensory feedback ~ Striatum Substantia Nigra Globus Pallidus Thalamus Cross section of Tegmentum Substantia Nigra Prefrontal Basal Ganglia M2 VLo M1 PPC Basal Ganglia Motor Loop Distal Limbs Basal Ganglia Movement Disorders Parkinson’s Disease 1% of population Nigrostriatal pathway Substantia nigra neurons die Progressive loss Hypokinesia Rigidity Bradykinesia Akinesia ~ Cortex + + Parkinson’s Disease Putamen + X SMA - Substantia Nigra Globus Pallidus (GPi) VLo - + Subthalamic Nucleus Parkinson’s Disease: Treatment Basal Ganglia - Cholinergic Substantia Nigra - Dopaminergic Drug Therapy L-DOPA Pallidectomy Tissue transplants ~ Huntington’s Disease (Chorea) Rare onset 30-40s early as 20s Degeneration of Striatum Caudate Putamen GABA & ACh neurons ~ Symptoms Khoros = dance Uncontrollable, jerky movements Dementia Progressive eventually fatal ~ + SMA Putamen X- Huntington’s Disease VLo - ++ GPe GPi - Subthalamic Nucleus Huntington’s Disease: Cause Genetic disorder Single dominant gene on chromosome 4 HD mutation unstable trinucleotide repeat - CAG # of repeats correlated w/ age of onset ~ Huntington’s Disease: Cause HD gene huntingtin 3 forms mutated form binds to protein involved in energy production neuron starves Excitotoxicity contributes to degeneration glutamate Nitric oxide (NO) Potential treatment:: Inhibit NO synthase ~ Hyperkinesia Excessive movement Ballism violent, flinging movements Lesions in subthalamus less inhibition of VLo excitation of SMA ~ SMA Striatum + Hyperkinesia (e.g. ballism) - VLo - Globus Pallidus + X Subthalamic Nucleus