* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KEY Combined Cells and Cell Divison Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
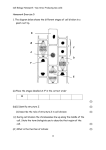
1. Refer to the illustration above. Which cell is most likely to lose both water molecules and solute molecules as the system approaches equilibrium? Number 4- because both water and solutes are high they will naturally diffuse to a low area. 2. Refer to the illustration above. In this system, solute molecules in cell 2 are most likely to diffuse to where? To cells 1 or 3 because they have a low concentration of solute 3. Refer to the illustration above. In which direction are water molecules in this system most likely to diffuse? (from cell 3 and 4 to cell 1 and 2 ) 4. If a cell swells when placed in a solution, the solution is a __hypotonic_____ solution. 5. If a cell is placed in salt water, water will leave the cell by what process? Osmosis 6. Name the 2 most important characteristic of facilitated diffusion? Requires no energy and requires protein 7. The net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration is called what? Diffusion 8. The concentration of a solution outside the cell is the same as inside the cell, thus there is no net movement of molecules. This is known as a Isotonic____ solution. 9. In the cell membrane, where are the fatty acid tails of phospholipid molecules located? Inside the bilayer because they are hydrophobic 10. How does water leave a cell when it is placed in salt water? Osmosis 11. What ability of the cell membrane prevents the inside of the cell from being exactly like the outside of a cell? Selective permeability 12. Sugar molecules can enter cells through what process? Facilitated Diffusion 13. What is the term that best describes the chapter that we have been studying? Life (cells which are the smallest unit of life) 14. “Homeostasis” or maintaining a balance is most associated with what cell structure? Cell membrane 15. The cell membrane is composed primarily of phospholipids. What part of the phospholipids is polar and what part is non-polar? Head-polar, tail- nonpolar Do the tails point outward toward the water, or inward away from the water? Inward Is the tail hydrophobic, or hydrophilic? Hydrophobic 16. The organelle found in the center of the cell, which contains the cell’s DNA is the what? Nucleus 17. A structure within a cell that performs a specific function is called an ___organelle_____. 18. Proteins are made by what organelle? Ribosomes 19. What is the packaging and distribution center of the cell? Golgi apparatus 20. In what organelle is a cell’s ATP (energy) produced? Mitochondira 21. The structure that regulates what enters and leaves the cell is called the what? Cell membrane 22. The vesicles containing digestive enzymes that break down proteins, waste, and cell parts, as well as destroys old cells when it is time for the cell to die are known as the what? Lysosome 23. The difference in smooth and rough ER is the presence or absence of what? ribosomes 24. The “framework” or network of thin tubes and filaments found within the cytoplasm that provide shape and support to the cell is known as the what? Cytoskeleton 25. Describe the functions of the cell membrane. To regulate what enters and exits the cell 26. What organelle functions as a sort of “intracellular highway”, a path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another? Endoplasmic Reticulum because it ships proteins to the Golgi 27. The smallest units of life in all living things are what? Cells 28. This organelle stores water, enzymes, and waste and can account for as much as 90% of the cells volume. Central Vacuole 29. This organelle is where the cell’s ribosomes are made. Nucleolus 30. This organelle is a rigid layer that is made of cellulose which forms a stiff box around the cell. Cell wall 31. This structure contains a system of flattened sacs (thylakoids) which contains the green pigment chlorophyll. Chloroplast 32. What are the organelles in plant cells that contain a green pigment? Chloroplast which contain chlorophyll Mitosis and Meiosis 1. What is a somatic cell? How many chromosomes does it have? A body cell with 46 chromosomes 2. What is a gamete? How many chromosomes does it have? A reproductive cell with 23 chromosomes 3. Give two examples of gamete cells Sperm and egg 4. What is the difference between a haploid cell, and a diploid cell? A diploid has a full set of chromosomes and haploid contains half 5. Draw a chromosome and label the following: chromosome, chromatid, centromeres. 6. Is a gamete cell haploid or diploid? Haploid 7. What are the sex chromosomes that make up a male? XY (hint: its 2 letters) 8. Diagram the process of fertilization (see your notes) and label the following: sperm cell, egg cell, zygote, haploid, diploid, 23, 46. 9. What is an “autosome”? Chromosomes not associated with the sex of an individual 10. What does monosomy and trisomy mean? Monosomy means one chromosome and trisomy means three (Downs Syndrome) 11. What is a karyotype? Picture of chromosomes 12. What is mitosis? How a cell divides to make identical cells 13. What are the 4 stages of mitosis? Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase 14. What is interphase, and what happens during this time? Interphase is normal cell activity, and DNA replication happens. 15. Diagram each of the 4 phases of mitosis and label the following: centrioles, spindles, chromosomes.