* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sections 3
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
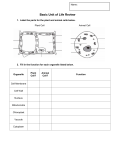
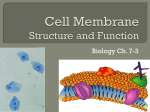
Chapter 3 Study Guide Section 3.1 1. What are the three parts of the cell theory? 2. Give two reasons why the cell theory is important. 3. Compare and contrast prokaryotic cells to eukaryotic cells. Discuss what they have in common and what is different between them. 4. What is cytoplasm? 5. Where do you find organelles? 6. Which types of cells have no nucleus? Section 3.2 Write either the function of the organelle or the name of each organelle. Draw a sketch to help you remember it. Organelle nucleus Function Sketch Helps in the production of proteins and lipids ribosomes Golgi apparatus Carries certain molecules from place to place within a cell mitochondrion vacuole lysosome centriole Section 3.3 1. Which type of molecule forms a lipid bilayer within a cell membrane?____________________________________ 2. Phospholipids are molecules that contain which of the following? a. b. c. d. phosphate nonpolar “tails” and polar “heads” form the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane all of the above 3. The structure that regulates what enters and leaves the cell is called the ____________ _____________. 4. The cell membrane allows some, but not all, molecules to cross. What term describes this property? _______________ ________________ Section 3.4 1. Define passive transport. 2. What are the types of passive transport we discussed in class? 3. What does semipermeable mean? 4. Which way do molecules move in passive transport? 5. Briefly describe the three types of solutions and how they affect the cell. Section 3.5 1. What is active transport? 2. What is the energy source that powers active transport? 3. What does active transport use to move substances? 4. Define endocytosis and provide an example. 5. Define exocytosis. Microscopes 1. Why do we need to use microscopes? 2. What are the three objective lenses (magnifications) you viewed the slides under? 3. How do you calculate total magnification? 4. Contrast magnification and resolution. 5. What type of microscope did you use in the lab?