* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure and Function of Cells
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
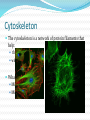
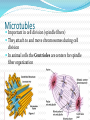
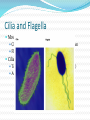
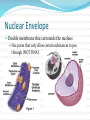
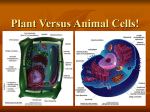
M. Tweedie Room 54 Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments that help: the cell retain its shape with cellular movement What are they? Microfilaments Microtubles Microfilaments Made of Actin (same protein found in muscle) Maintain cell shape Aide in movement Move the Pseudopod (false foot): projections of the cell membrane of eukaryotes Microtubles Important in cell division (spindle fibers) They attach to and move chromosomes during cell division In animal cells the Centrioles are centers for spindle fiber organization Cilia and Flagella Move the Cell Cilia – tiny hair-like projections that beat in rhythm Flagella – whip-like projections Cilia can also be used: To move substances along surface (lining of lungs) As sensory receptors (touch, sound, etc.) Nuclear Envelope Double membrane that surrounds the nucleus Has pores that only allow certain substances to pas through (NOT DNA!) Cell Wall Plants have a cell wall surrounding their cell membranes Made of Cellulose (polysaccharide) Gives structure and support Works with central vacuole to hold plant upright (pressure inside) Turgor Pressure in Plants!