* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Table of nitrogen base
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
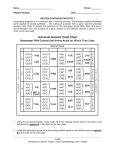
©Thomas and Karen Booker Alien Protein Synthesis Pre-Lab Reading Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics, like hair color and blood type. Genes are composed of DNA. The DNA code is based on a triplet of nitrogen bases. The triplet code codes for a specific amino acid. Amino acids combine to form proteins. In a process known as transcription (takes place in the nucleus) messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA. mRNA then takes this message out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm to the ribosome (rRNA), the site of protein synthesis in a process known as translation. It is at the ribosome that the third form of RNA arrives, transfer RNA (tRNA). Transfer RNA carries a specific amino acid for a specific codon on the mRNA. The tRNA binds to the mRNA by the anti-codon. This continues until a protein has been manufactured. In this activity you have collected a sample of alien DNA from a distant planet. This species has 8 genes that you have designated: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8. Transcribe the DNA into mRNA, then find the anti-codon and the corresponding amino acid. The series of amino acids will determine the protein (trait). Problem: How are an organisms’ traits determined? How do the genes ultimately result in a characteristic? Procedure: 1. To determine the trait for Gene #1 of your alien, write down the DNA sequence from the overhead. 2. Use the Table of nitrogen base pairings to determine the mRNA for Gene #1 of your alien. 3. Use the Table of nitrogen base pairings to determine the tRNA for Gene #1 of your alien. 4. To determine the amino acid sequence, match the tRNA anticodon with the amino acid coded for it, based on the tRNAs below. 5. The amino acids will combine to form a protein (trait). 6. Repeat steps 1 - 5 for each gene, then draw your alien! Table of nitrogen base-pairings DNA DNA DNA mRNA mRNA tRNA TA TA U* A AT A U* A U* GC GC GC CG CG CG Phe Leu Ile Start Val Ser Pro Thr Ala Try Stop His Gln Asn Lys Asp Glu Cys Arg Trp AAA GAG UAA UAC CAC AGU GGG UGA CGG AUA AUC GUG GUU UUA UUU CUA CUC ACA GCC ACC Amino Acids Start-Ser-His-Asn-Asp-Arg-Pro-Stop Start-Try-Ala-Val-Leu-Gln-Glu-Stop Start-Arg-Arg-His-Ser-Stop Start-Phe-Leu-Val-Pro-Stop Start-Cys-Asp-Asn-His-Try-Thr-Ser-Stop Start-Ile-Val-Pro-Asn-His-His-Asp-Stop Start-Val-Val-Stop Start-Arg-Arg-Stop Start-Phe-Ile-Pro-Gln-Asp-Cys-Stop Start-Phe-Trp-Ile-Pro-Gln-Asp-Stop Start-Try-His-Stop Start-Pro-Ile-Stop Start-Try-Ala-Gln-Ser-Lys-Ile-Cys-Stop Start-Phe-Arg-Ile-Cys-Val-Glu-Ser-Stop Start-Gln-Asn-Lys-Stop Start-Thr-Ala-Try-Stop Proteins (Traits) green skin blue hair big, pointy teeth long, quick tongue 3 arms no arms 9 legs snakelike body horns antennae 3 eyes 9 eyes sharp claws suction cups on fingers wings scaly plates on back Amino Acid anticodon tRNA ©Thomas and Karen Booker Name Period Data Tables Alien #: Gene # 1 Gene # 2 DNA mRNA tRNA DNA mRNA tRNA Amino Acids Protein (trait) Amino Acids Protein (trait) Gene # 3 Gene # 4 DNA mRNA tRNA DNA mRNA tRNA Amino Acids Protein (trait) Amino Acids Protein (trait) Gene # 5 Gene # 6 DNA mRNA tRNA DNA mRNA tRNA Amino Acids Protein (trait) Amino Acids Protein (trait) Gene # 7 Gene # 8 DNA mRNA tRNA DNA mRNA tRNA Amino Acids Protein (trait) Amino Acids Protein (trait) Sketch Your Alien! Analysis & Conclusions Briefly describe the steps in Protein Synthesis. Describe all 3 forms of RNA and discuss their functions. Describe how you could find the DNA if you knew the amino acid sequence. Give an example to illustrate your point. Could a mutation in the DNA affect the way an organism looks? Give an example to illustrate your point. ©Thomas and Karen Booker Alien Name: ©Thomas and Karen Booker Recovered Alien DNA Sequences Species 4672-A Gene 1: TAC-AGT-GTG-TTA-CTA-GCC-GGG-ATC Gene 2: TAC-AAA-GAG-CAC-GGG-ATC Gene 3: TAC-ACA-CTA-TTA-GTG-ATA-TGA-AGT-ATC Gene 4: TAC-GCC-GCC-ATC Gene 5: TAC-AAA-TAA-GGG-GTT-CTA-ACA-ATC Gene 6: TAC-ATA-GTG-ATC Gene 7: TAC-AAA-GCC-TAA-ACA-CAC-CTC-AGT-ATC Gene 8: TAC-TGA-CGG-ATA-ATC Species 4672-B Gene 1: TAC-ATA-CGG-CAC-GAG-GTT-CTC-ATC Gene 2: TAC-GCC-GCC-GTG-AGT-ATC Gene 3: TAC-TAA-CAC-GGG-TTA-GTG-GTG-CTA-ATC Gene 4: TAC-CAC-CAC-ATC Gene 5: TAC-AAA-ACC-TAA-GGG-GTT-CTA-ATC Gene 6: TAC-GGG-TAA-ATC Gene 7: TAC-ATA-CGG-GTT-AGT-TTT-TAA-ACA-ATC Gene 8: TAC-GTT-TTA-TTT-ATC