* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genome Shock in Polyploid Plants
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Human–animal hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
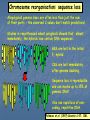
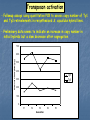
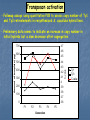
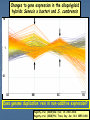
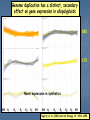
Genome Shock in Polyploid Plants Matt Hegarty The importance of polyploidy • It is predicted that ~70% of higher plants have undergone at least one round of genome duplication over their evolutionary history. • Approximately 2-4% of speciation events involve a change in ploidy. • It is estimated that the majority of polyploid species are the result of interspecific hybridisation. • Polyploids represent a source of genetic novelty upon which selection may act. • Many of the world's most successful crop species are polyploids (bread wheat, coffee, cotton, sugarcane, maize) and often significantly outperform their diploid relatives. Hybrid speciation in Senecio: the allopolyploid origin of S. cambrensis X Senecio squalidus Diploid, SI Known to have occurred at least TWICE Senecio vulgaris Tetraploid, SC Senecio x baxteri Triploid, sterile Chromosome doubling Senecio cambrensis Hexaploid, fertile, SC What are the genetic consequences of polyploidy? • Genetic changes as a consequence of uniting 2+ divergent genomes within a single hybrid nucleus: 1) new combinations of gene regulatory networks. Arabidopsis thaliana 2n=2x=10 X A. arenosa 2n=4x=32 Unreduced gamete A. suecica 2n=4x=26 FRI FLC FRI FLC A. thaliana A. arenosa Wang et al. (2006) Genetics 173: 965-974 2) Recombination: rapid recombination is often seen in hybrids - serves to resolve chromosomal incompatibilities in homoploids and reinforce reproductive isolation. - in allopolyploids, helps prevent mispairing of homoeologous chromosomes. Chromosome reorganisation: sequence loss • Allopolyploid genome sizes are often less than just the sum of their parts - the observed C values don‟t match predictions! • Studies in resynthesised wheat polyploids showed that, almost immediately, the hybrids lose certain DNA sequences: GSS are lost in the initial F1 hybrid. CSS are lost immediately after genome doubling. Sequence loss is reproducible and can involve up to 15% of genomic DNA! Also see rapid loss of noncoding, repetitive DNA. Feldman et al. (1997) Genetics 147: 1381. Transposon activation • McClintock predicted widespread activation of transposable elements as a consequence of the “genomic shock” of hybridisation. • Transposon activity would facilitate rapid recombination by increasing the likelihood of chromosome breakage. • Also has the potential to alter gene expression. S. aethnensis S. chrys. S. squalidus S. aethnensis S. chrys. S. squalidus Transposon activation • Followup assays using quantitative PCR to assess copy number of Ty1 and Ty3 retroelements in resynthesised S. squalidus hybrid lines. • Preliminary data seems to indicate an increase in copy number in initial hybrids but a slow decrease after segregation. 700 Amount of template (pg) 600 500 400 Ty1 Ty3 300 200 100 0 F1 F2 F3 Generation F4 F5 Transposon activation • Followup assays using quantitative PCR to assess copy number of Ty1 and Ty3 retroelements in resynthesised S. squalidus hybrid lines. • Preliminary data seems to indicate an increase in copy number in initial hybrids but a slow decrease after segregation. 4.7 4.6 600 4.5 4.4 500 4.3 400 4.2 300 4.1 4 200 3.9 3.8 100 3.7 0 3.6 F1 F2 F3 Generation F4 F5 C-value Amount of template (pg) 700 Ty1 Ty3 C-value Changes to gene expression in the allopolyploid hybrids Senecio x baxteri and S. cambrensis 10 1 0.1 SS SB SC SV Does genome duplication „rein in‟ non-additive expression? Hegarty et al. (2005) Mol. Ecol. 14: 2493-2510. Hegarty et al. (2008) Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. 363: 3055-3069. Genome duplication has a distinct, secondary effect on gene expression in allopolyploids 58% 17% Novel expression in synthetics SB S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 SC SB S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 SC Hegarty et al. (2006) Current Biology 16: 1652-1659. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression • Studies in allopolyploid systems show rapid changes to DNA methylation and histone acetylation relative to parental taxa. - Early work in Arabidopsis using cDNA-AFLP showed silencing of a number of genes in the allotetraploid hybrid. - This was tested further using MSAP and 8.3% of loci showed differential methylation between the parents and an F3 hybrid. • Similar findings have been made in systems such as Spartina (up to 30% of loci affected!) and wheat (13%). • These changes may serve to prevent expression of duplicated gene copies where this would be counterproductive. • In an extreme example, the genes affected in A. suecica hybrids are the rRNA genes of the A. thaliana parent, causing almost total suppression of A. thaliana gene expression - nucleolar dominance. • Very little information on the role of miRNA/siRNAs in hybrids... Investigating DNA methylation in Senecio using MSAP • MSAP = modified AFLP using EcoRI and either HpaII or MspI. • If a locus is methylated will see a shift in AFLP profile. HpaII In this example the peak in the MspI sample but not HpaII indicates methylation at the CCGG recognition sequence of this locus. MspI Currently analysing data from an analysis of three synthetic lines of S. x baxteri and two generations of their allohexaploid derivatives plus the parental taxa. Subfunctionalisation - a basis for heterosis? • Studies in allotetraploid cotton (and recently wheat) showed that gene copies from different parents had different expression patterns. • What they observed was organspecific reciprocal silencing of one parental gene copy. • When assessed in new hybrids, they found that these patterns were replicated. A genome copy D genome copy • More importantly, they observed that relative expression of the parental gene copies could vary based on environmental stress. • This could allow polyploids to „select‟ the best gene copy to express in a given environment - maybe why polyploids are so successful? cDNA-SSCP PCR is used to amplify a small segment of the gene of interest containing a SNP that can be used to identify parental origin. These secondary structures migrate at different rates, so sequence variants can be identified by differences in banding patterns. S. vulgaris S. squalidus …CACCG…GGTTC… ...CAGCG…GGGTC… hfr2 - Hessian Fly Resistance gene gDNA cDNA SV SS AC Bax SV SS AC Bax • Upregulated in S. squalidus relative to all other taxa according to array data. • S. vulgaris specific band, while inherited in the hybrids, is silenced. • SSCP hybrid expression pattern favours S. squalidus. Future work • Next-generation sequencing in Senecio - funded for a single run using CRoPS to identify polymorphisms between allopolyploids and parents. Also awaiting decision on NERC proposal. • Other allopolyploid systems - festulolium, white clover. Festulolium = grass hybrid of Lolium perenne X Festuca pratensis IBERS have a number of hybrid/ introgression lines Genetics well-characterised Natural hybrids exist, may have improved flood tolerance Images from Humphreys & Harper (2008) Crop Wild Relative 6:1-3. Synteny with other grasses Acknowledgements University of Bristol: University of St. Andrews: Simon Hiscock (PI) Richard Abbott (Co-I) Keith Edwards (Co-I) Adrian Brennan (Postdoc) Gary Barker (Bioinformatics) Jane Coghill (Transcriptomics) Chris Thorogood & Sacha Allen (Ph.D students) Tom Batstone (Technician) Aberystwyth University: Wayne Powell (Director) Charly Morgan (Technician) Research Funding: NERC Linnean Society