* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Vacuole - Konner Aldridge Enterprises
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
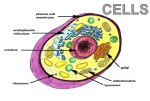
Aldridge 1 Konner Aldridge Mr. Bryant Biology- B4 04 December 2012 Vacuoles: The Storage Bin of the Cell The vacuole is found within plant, animal, fungal, and bacterial cells and they serve a vital purpose in each. They are found in hollowed center regions of the cell, and can be very large in plant cells. The vacuole provides help with intracellular digestion and helps the release and effective use of cellular waste. The vacuole is considered to be the “storage bin” of the cell. (Shashank, 2012) The vacuole collects waste within the cell to protect the other organelles from the harmful effects of the waste by destroying the harmful bacteria found within it. The vacuole also plays a major role in the growth and development of plants and plant cells. The vacuole was first discovered by Anton Van Leeuwenhoek on January 25th, 1676. It is believed that he made his discovery in the Netherlands since he made many other discoveries in that same place in 1675 and 1676. Because Leeuwenhoek made so many discoveries in such a short period of time, there are no specific articles or documentation that state the details of his discovery. Leeuwenhoek, who is considered “the father of microscopy,” was a Dutch scientist who lived in the Netherlands and discovered many things such as protozoa, the red blood cell description, infusoria, bacteria, and muscle fibers all within about 15 years. With so many discoveries made so quickly, documentation was not made. Vacuoles are found in central and hollow parts of the cell. They are forced by the fusion of multiple membrane vesicles. Vacuoles do not have a distinct shape or size and can take up to Aldridge 2 90% of the space found in a mature plant cell. They contain a liquid called sap, which contains enzymes and compounds necessary to the functionality of the cells. The vacuole also contains mixtures of things such as sugars, salts, pigments, gases, and acids which can be found in the center of the organelle. In the early stages of a plant cell, it will contain multiple small vacuoles and will eventually increase in size and combine together to create a large centrally located vacuole used for storage. Because the vacuole eventually increases in size and becomes very large, it pushes other organelles such as the chloroplasts and nucleus against the cell wall and the cell membrane. This helps a plant to grow and become healthier. Vacuoles play a huge role in digestion and waste management within the cell. They store nutrients and waste for the cell, they help “increase cell size during growth” and they can tend to act like lysosomes (which are found in animal cells) for the plant cell. Vacuoles collect water within the cell. Vacuoles also regulate turgor pressure within the cell. Turgor pressure is regulated by the amount of water and materials collected in the cell vacuole. The more water it has, the more the vacuole will push against the cell wall and other organelles, causing the plant to grow, become rigid, and stand up straight. If the vacuole does not contain enough water, the plant will die due to low turgor pressure. The vacuole manages the pH level of the liquid of the cell and hydrostatic pressure is maintained by the vacuole. The vacuole is also a source of protection for the cell and all of the other organelles found within the cell. It breaks down and filters waste and any other material and takes out all of the harmful substances that can be generated through cell waste. Vacuoles will then quarantine the substances and destroy the unwanted substances in the cell. The vacuole is much more useful in the plant cell than it is in the animal cell. The vacuole is a major factor in the growth of a plant and controls all of the water intake and control turgor pressure. Plant cells contain vacuoles that are much larger in size Aldridge 3 than any other cell. If a cell contained no vacuole, it would not be able to function and it would die. It protects all other organelles from the harmful substances found in the liquids and wastes found within a cell. Without the vacuole filtering the waste, the other organelles would become poisoned by the contaminants and would not be able to function. Also, in plant cells, the vacuole is needed to collect water and control turgor pressure. If there were no vacuole present in the plant cell, the plant would not grow and it would wilt and die because nothing would collect the water and help support the plant. Without the vacuole, a cell would be useless and non-existent because they would not be able to function and support themselves. If the cell was compared to a city, I would describe the vacuole as being either the warehouses, water towers, or garbage dumps. It would be described as a warehouse because of its ability to store and hold anything that the cell needs such as waste and water for the cell to grow. It can be described as a water tower because the vacuole holds and contains all the water found within the cell and uses it to help the cell function. It can also be described as the garbage dumps (or landfill) because it is where all the waste and unwanted materials found within a cell are contained. The vacuole then takes the unwanted material and holds it or destroys anything harmful to other organelles around it. The vacuole has a very important function within the cell! The vacuole has a very important and diverse role within the cell. It was discovered by Anton Van Leeuwenhoek in the late 1600’s and described as a sac-like organelle found within the cytoplasm of the cell. It is extremely vital and an essential need of the plant cell. Without a vacuole, a cell would not survive. It maintains and controls the turgor pressure within the plant cell, which determines how well a plant develops and grows. The vacuole is found in the center of the cell and contains things such as sugars, acids, and pigments. It is a storage center and helps with internal digestion and controls the waste management process needed for the cell. Aldridge 4 The vacuole contains all the water that is needed for the cell to function. It takes up over 90% of the space found in the plant cell. It is a major need of the cell and is necessary for the cell to survive. Aldridge 5 Transmission Electron Micrograph picture of the vacuole: Aldridge 6 Works Cited "Anton Van Leeuwenhoek." Wikipedia. Wikimedia Foundation, 15 Nov. 2012. Web. 02 Dec. 2012. <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anton_Van_Leeuwenhoek>. Khan, Dr. Sumaiya. "Vacuole Structure." Buzzle.com. Buzzle.com, 02 Dec. 2010. Web. 02 Dec. 2012. <http://www.buzzle.com/articles/vacuole-structure.html>. Leigh, R. A., and D. Sanders. "Section 4: Function." The Plant Vacuole. 3rd ed. San Diego: Academic, 1997. 24-33. Print. Nakate, Shashank. "Vacuole Function." Buzzle.com. Buzzle.com, 25 July 2012. Web. 02 Dec. 2012. <http://www.buzzle.com/articles/vacuole-function.html>. "Vacuoles - Storage Bins to the Cells." Biology4Kids.com: Cell Structure: Vacuoles. Andrew Rader Studios, 2003. Web. 02 Dec. 2012. <http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_vacuole.html>.