* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PARTS OF ALL CELLS: PARTS OF PLANT CELLS ONLY:
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
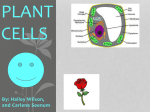
CellsThe building blocks of all living things. Cell theory: (3 rules about cells) 1. Cells carry out all life processes (releasing carbon dioxide, taking in oxygen, and giving off energy) 2. All living things are made up of cells 3. New cells come from existing cells. (cells reproduce) PARTS OF ALL CELLS: NUCLEUS-Brain of the cell; controls all cell activity CELL MEMBRANE- Door of the cell; controls what enters and leaves the cell (lets the good stuff in, keeps the bad stuff out) CYTOPLASM- Jelly-like substance that fills the cell; holds all the organelles in place VACUOLE- Storage space of a cell. Stores water, food, and waste. PARTS OF PLANT CELLS ONLY: (Note: Plant cells have parts that animal cells do not have because plants have a special task to do….THEY MAKE THEIR OWN FOOD) CELL WALL- Provides an extra layer of support for the plant cell. CHLOROPLAST- Contains chlorophyll, place where the plant makes its own food. That food is called GLUCOSE. LARGER VACUOLE- Needed for extra storage space. Plants need more H2O to make its own food. Q1. What is a cell? Q2. Name the three facts of the cell theory. Q3. What is the difference between the shape of an animal cell and the shape of a plant cell? Q4. Name the two parts that a plant cell has that an animal cell does NOT. Q5. What is the function of the cell wall? Q6. Describe the function of the chloroplasts. Q7. What part of the cell acts like the “brain” of the cell? Why is it called the brain of the cell? Q8. What part of the cell controls what enters and leaves the cell? Q9. Describe the job of the vacuole. Q10. A plant cell has a larger vacuole than the animal cell. Why? Q11. What part of the cell is the jelly-like substance that holds all of its parts in place? Q12. What is the hard, protective surface that surrounds the plant cell and provides extra support? Q13. Label the animal cell below. Q14. Label the plant cell below. WORDS TO USE: VACUOLE, NUCLEUS, CELL MEMBRANE, CYTOPLASM, MITOCHONDRIA WORDS TO USE: VACUOLE, NUCLEUS, CELL MEMBRANE, CYTOPLASM, MITOCHONDRIA, CHLOROPLAST, CELL WALL