* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Transport Vocabulary
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
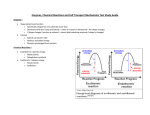
Cellular Transport Vocabulary 1. Homeostasis—a balance of substances within the cell 2. Protein-lipid bilayer—two layers of phospholipids with proteins; describes the cell membrane 3. Fluid mosaic model—describes the cell membrane as being made of similar molecules (lipids) which freely move within the membrane 4. Selectively permeable (semi-permeable)—controls what enters and exits the cell 5. Protein markers—allow the cell to communicate with other cells 6. Transport proteins—allow big substances or certain ions to move through the membrane 7. Cholesterol—very rigid molecules that strengthen the cell membrane 8. Hydrophilic heads—the part of the phospholipids that attracts water 9. Hydrophobic tails—the part of the phospholipids that repel water 10. Passive Transport—transport that requires NO ENERGY from a cell 11. Simple diffusion—the movement of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 12. Concentration gradient—differences in concentration 13. Osmosis—diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane 14. Isotonic—has a concentration equal to the concentration inside the cell; results in no change in a cell 15. Hypotonic—has a concentration lower than the concentration inside the cell; results in the cell swelling 16. Hypertonic—has a concentration higher than the concentration inside the cell; results in a cell shrinking or shriveling 17. Turgor pressure—pressure inside a cell 18. Cytolysis—cell bursts, which causes cell death 19. Contractile vacuole—special organelle in some protists that pumps excess water out of the cell to keep cell from bursting 20. Plasmolysis—cell shrinks or shrivels due to water loss 21. Facilitated diffusion—passive transport that requires a transport protein 22. Active Transport—transport that requires energy from a cell 23. Ion pumps—carrier proteins that move ions through membrane 24. Endocytosis—active transport in which the cell engulfs a particle or substance using a vesicle 25. Phagocytosis—type of endocytosis in which the cell engulfs a large solid; “cell eating” 26. Pinocytosis— type of endocytosis in which the cell engulfs a liquid or tiny solid; “cell drinking” 27. Exocytosis—active transport in which the cell pushes a substance/particle out of the cell with the use of a vesicle