* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 08
Stingray phone tracker wikipedia , lookup
Cryptographic hash function wikipedia , lookup
Trusted Computing wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Authentication wikipedia , lookup
Next-Generation Secure Computing Base wikipedia , lookup
Electronic authentication wikipedia , lookup
Pretty Good Privacy wikipedia , lookup
Secure multi-party computation wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Security and safety features new to Windows Vista wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Block cipher wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Digital signature wikipedia , lookup
One-time pad wikipedia , lookup
Public-key cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Certificate authority wikipedia , lookup
Index of cryptography articles wikipedia , lookup
Cybercrime countermeasures wikipedia , lookup
Diffie–Hellman key exchange wikipedia , lookup
Web of trust wikipedia , lookup
Cryptanalysis wikipedia , lookup
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
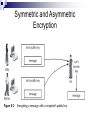
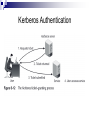
Linux Networking and Security Chapter 8 Making Data Secure Making Data Secure Explain commonly used cryptographic systems Understand digital certificates and certificate authorities Use the PGP and GPG data-encryption utilities Describe different ways in which cryptography is applied to make computer systems more secure Cryptography and Computer Security Computer security is about making certain that the only people accessing resources or data are those whom should have access Cryptography is the science of encoding data so that it cannot be read without special knowledge or tools; it is a key part of network applications and normally hidden from view Network connections can be tapped to allow for viewing of transmitted data - called sniffing the network, and encryption can block this Cryptography and Computer Security Basic Encoding Techniques The process of cryptography is as follows: Begin with the message to transmit - called the plaintext Apply a technique or rule called a cipher to change the plaintext The result is ciphertext, an encrypted message The most elementary example of encryption is lettersubstitution where a different letter of the alphabet is substituted for each letter in the message Key Systems Rules, known as algorithms, allow letter-substitution to convert plaintext to ciphertext The level of complexity of an algorithm can be increased by using a key, a code necessary to encrypt or decrypt a message correctly using the algorithm Knowing the algorithm (the cipher) should not enable readability; good security assumes an eavesdropper knows the cipher, but the key must be kept secret DES The Data Encryption Standard (DES) was developed in the 1970s and uses a 56-bit key to encrypt data using various algorithms 56 bits provide for 256 possible keys It now takes 20 hours to break a DES key DES is being phased out, but it is still widely used since relatively few people have the equipment to break the key, 20 hours is still a relatively long time in the Internet age, and it was a widely implemented U.S. standard Skipjack and Triple DES There were several responses to the cracking of DES: DES keys were increased to 1024 bits Creation of a new algorithm called Skipjack, which uses an 80 bit key Triple DES relies on DES, but encodes each message three times using three different keys Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) can provide roughly 1077 possible keys, and was approved for use by U.S. government agencies in May 2002 Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption Symmetric encryption algorithms Use the same key and algorithm to encrypt and decrypt a message The key used is called a private key, because it must be kept secret for the message to be secure Asymmetric encryption algorithms Use one key to encrypt and another to decrypt The key you can reveal to everyone is called a public key Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption Signatures and Certificates Authentication is the process of proving that you are in fact the person you say you are Signatures let you authenticate a public key You sign another person’s public key with your own private key to verify that the key really belongs to that person Certificates provide the same type of verification as signatures A certificate is a numeric code that is used to identify an organization Signatures and Certificates Signatures and Certificates Fingerprints A fingerprint is a smaller number that is derived from a very lengthy public key Fingerprints are created by hashing the public key, a process by which a mathematical function is used that converts larger numbers into smaller numbers Two commonly used hashes: Message digest hash (MD5) provides 128 bits Secure hash algorithm (SHA-1) provides 160 bits Using Cryptography in a Browser Whenever you visit a Web page that has been transmitted to your computer using encryption, you see a small lock or key in the lower left corner of the browser window Most encrypted Web pages, such as order-entry screens, shopping carts, and similar data, appear with a URL that starts with https The encrypted protocol for Web pages is Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Using Cryptography in a Browser Using Cryptography in a Browser Using Cryptography in a Browser Using Cryptography in a Browser Kerberos Authentication Kerberos authentication is a special kind of authentication for organizational networks Kerberos was developed at MIT and is widely used around the world Kerberos secures a network by providing a system that makes users prove who they are before they can use a service and also makes services prove who they are It uses both public-key cryptography and a symmetric cipher Kerberos Authentication Kerberos Authentication Kerberos Authentication Using Encryption Utilities Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) is the first utility to provide public-key encryption to all Although PGP software was formerly included in Linux, it has been replaced with GPG Gnu Privacy Guard (GPG) is a public-key encryption utility and uses non-patented algorithms GPG operates from the command line, but there are graphical utilities to make it easier to use Using Encryption Utilities Using Encryption Utilities Other Security Applications RPM security can check a public-key signature on any package to verify that it came from its stated creator Cryptographic File System (CFS) enforces cryptographic authentication on all users who want to share files across the network Transparent Cryptographic File System (TCFS) operates transparently to users IPSec and CIPE provide for IP packet encryption Secure Shell Secure Shell (SSH) is an encrypted version of Telnet, which provides secure remote access SSH allows other protocols to ride on top of it A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a secure organizational network that uses an insecure public network (Internet) for communications VPNs are often created with the aid of specially designed software that integrates many networking functions with cryptographic protocols and system management software Virtual Private Networks Chapter Summary Cryptography is the science of encoding data, typically using a key, so that people without the key cannot read the data Cryptography protects computer networks against sniffers, programs that allow crackers to see data passing along a network Many different algorithms are used to encrypt data and they are either symmetric or asymmetric DES was a popular standard algorithm for years, until Triple DES and AES began to replace it Chapter Summary Public-key encryption does not require that you openly exchange a secret key with the recipient of an encrypted message RSA is the most familiar public-key algorithm Signatures on a document show that the sender is the only one who could have sent the document Certificates are issued and signed by certificate authorities such as VeriSign to vouch for the identity of the organization holding the certificate Chapter Summary A hash is a mathematical function that creates a small number from a very large number and it is used to create a fingerprint Browsers such as Netscape and Mozilla use cryptography via the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol to allow secure ecommerce transactions Kerberos provides a network-wide user and service authentication scheme to limit network access to authorized users PGP was the first freely available public-key encryption software and remains an industry standard on which GPG is based Chapter Summary The Gnu Privacy Guard (GPG) is a free public-key encryption utility that lets you manage keys and encrypt, sign and decrypt documents Keys should be signed only when the identity of the person providing the key has been ascertained with certainty The rpm utility can check a public key signature on any package to verify that it came from the person or organization that claims to have created it Chapter Summary Other security protocols built on the same principles of cryptography as GPG include IPsec, CIPE, CFS and TCFS The Secure Shell (SSH) provides encrypted remote access via a utility that functions like Telnet. SSH also lets other protocols work with it to create secure connections for many purposes