* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membranes
Survey
Document related concepts
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
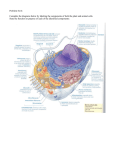
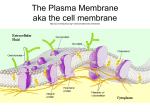
CELL MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION FLUID MOSAICS OF LIPIDS AND PROTEINS COMPOSITION Phospholipids Give membrane hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties Phosphate – hydrophilic, face aqueous exterior or interior Fatty acid – hydrophobic, face each other inside the membrane Proteins Cholesterol, Glycolipids, and Glycoproteins COMPOSITION Phospholipids Proteins: many different roles Hydrophilic Have charged and polar side groups Hydrophobic Have nonpolar side groups Cholesterol, Glycolipids, and Glycoproteins COMPOSITION Phospholipids Proteins Cholesterol, Glycolipids, and Glycoproteins Cholesterol: resists changes in membrane fluidity caused by changes in temperature Glycolipids & Glycoproteins: have a carbohydrate attached; cell-cell recognition SELECTIVE PERMEABILITY THE PURPOSE: TO SEPARATE THE INTERNAL FROM THE EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT Can Pass Through: Small, Uncharged polar Small Nonpolar Can NOT Pass Through (without assistance): Hydrophilic Large Polar Ions Water substances Note: Plant Cell Walls are made of cellulose and are external to the cell membrane. They are also found in Prokaryotes and Fungi. PASSIVE AND ACTIVE TRANSPORT PASSIVE TRANSPORT Does not require the input of energy Net movement of molecules from high to low concentration Used to import resources and export wastes Water moves across the membrane through proteins called “aquaporins.” Osmosis: the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Tonicity: the ability of a solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water PASSIVE TRANSPORT Solutions Isotonic outside a cell may be… – same concentration of solutes as the interior of the cell; water moves across membrane at the same rate in both directions KEY: term – exterior solution; effect – direction of water flow PASSIVE TRANSPORT Solutions outside a cell may be… Hypotonic – lower concentration of solute than the interior of the cell; water moves across membrane into the cell faster than it flows out, causing it to swell and lyse (burst) KEY: term – exterior solution; effect – direction of water flow PASSIVE TRANSPORT Solutions outside a cell may be… Hypertonic - higher concentration of solute than the interior of the cell; water moves across membrane out of the cell faster than it flows in, causing it to shrivel and possibly die KEY: term – exterior solution; effect – direction of water flow ACTIVE TRANSPORT Requires energy to move molecules from low to high concentration Free energy often from ATP Uses membrane proteins Example: Sodium-potassium pump EXOCYTOSIS AND ENDOCYTOSIS MOVING LARGE MOLECULES BETWEEN THE INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT Exocytosis – internal vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane to secrete macromolecules out of the cell Endocytosis – the cell takes in macromolecules and other particles by forming vesicles from the plasma membrane