* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to drugs and the brain
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
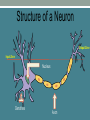
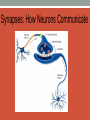
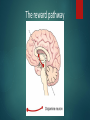
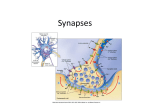
Drugs and Your Brain UCLA NS 192C Spring 2015 The Basics What is the Brain? The Brain • Contains 1 trillion cells • One neuron can have up to 1500 synapses • Consistency of hard Jell-O • When awake, your brain produces enough electricity to power a small light bulb Structure of a Neuron Output Zone Input Zone Nucleus Dendrites Axon Synapses: How Neurons Communicate Neurotransmitter-Receptor Binding: The Lock and Key Neurotransmitter-Receptor Binding: The Lock and Key Serotonin and Dopamine Involved in: ● Reward ● Mood ● Pleasure/pain ● Learning & memory Drug Use, Abuse, and Addiction 1. Opiates 2. Hallucinogens 3. Stimulants 4. Depressants 5. Cannabinoids 6. Date rape drugs 7. Dissociatives 8. Prescription drugs 9. Inhalants Drug Categories Why Do People Take Drugs? Why Do People Take Drugs? ● ● ● ● ● ● ● “It feels good” To fit in Curiosity To escape reality Help with illness Relieve pain Enhance performance (academic, sports, etc) The reward pathway Drugs Can Change Brain Circuitry Drugs can “hijack” the brain’s natural connections and change them, which can cause a variety of consequences Addiction You’re no longer in control...The drug controls you