* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7 Reading Guide
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
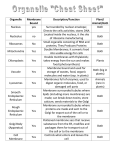
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure & Function Reading Guide Name:________________________________ Period:_______ Date:___________________ Use the information in Chapter 7 (p.125-139) as well as the Bozeman podcasts on the Cell Membrane and Transport Across Cell Membranes to complete the reading guide. Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins Draw and label a single phospholipid molecule. Explain why these molecules are amphipathic and how that enables them to form a lipid bilayer. Why must membrane proteins be amphipathic like the phospholipids? Produce a detailed, labeled drawing of the plasma membrane (Figure 7.5) in the space below. Discuss how evolution has favored different membrane lipid composition. Complete the following table to organize the various functions of membrane proteins (Figure 7.10). Function Description Diagram Transport Enzymatic Activity Signal Transduction Cell-Cell Recognition Intercellular Joining Attachment to ECM Concept 7.2 Membrane structure results in selective permeability How does membrane structure allow selective permeability? Describe the role of a transport protein and discuss the function of an aquaporin. Concept 7.3 Passive transport is diffusion of a substance across a membrane Explain how diffusion works to restore equilibrium across a permeable membrane. Include a diagram to help your explanations. Discuss how a hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic solution would impact the tonacity of an animal and plant cell. Include a diagram to help your explanations. Compare and contrast the structure and function of channel proteins and carrier proteins. Concept 7.4: Active transport uses energy to move against gradients Discuss how active transport differs from facilitated diffusion. Describe an example of active transport in a plant and an animal cell and include diagram to help your explanation. Describe the process of exocytosis and endocytosis. Include a diagram to help your explanations.