* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microtubules and Microfilaments
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
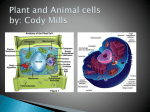
Plasma Membrane • Helps maintain Homeostasis • Present in all cells • Flexible boundary between the cell and its environment to allow nutrients and wastes to enter and exit Cytoskeleton • Supportive network of proteins that helps to form a frame work for cells – Just like your skeleton supports YOU! • Composed of rods/filaments (Microtubules and Microfilaments) that can be rearranged to meet the needs of the cell – Think of poles that maintain the shape of a tent. • They also help to anchor and support many organelles and provide a highway system through which materials move in and out of the cell. • Found in BOTH! Microtubules/Microfilaments • Thin hollow tubes made of proteins • Acts as “tracks” to move organelles • Smaller, solid protein fibers – Think of small threads • Enable the cell to move and divide • Help muscles contract and relax Work together Both work to anchor and support many organelles Provides a highway system for materials to move within a cell Microfilaments/Microtubules Cytoplasm • fills the space between the nucleus and the cell membrane • Clear, gelatinous fluid portion is called cytosol and is mainly water • Location of all other organelles • Found in all Cells Nucleus • Cell Control Center • Contains the directions to make proteins • Two main jobs is to protect the DNA and make sure that DNA is always available for use. • Found in all cells Nuclear Membrane and Nuclear Pores • Located outside of the nucleus • Also called Nuclear envelope • Made up of a double membrane containing two phospholipid bilayers • Contains small nuclear pores – Allow substances to pass from the nucleus to cytoplasm Nucleolus • Located within the nucleus • Responsible for making ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum • A folded membrane that forms a network of interconnected compartments in the cytoplasm • The location of cellular chemical reactions • Found in Both types of cells • Rough ER – contains ribosomes that are attached to the surface, it is involved in the transport, storage, making and modifying of proteins. • Smooth ER- production and storage of lipids, contains NO ribosomes Ribosomes • Site of protein synthesis (make proteins) – They link amino acids together • Can be found floating in the cytoplasm, BUT most of the time they attach to the Endoplasmic Reticulum • Found in all cells Golgi Apparatus • Closely stacked, flattened membrane sacs • Modify, collect, and sort proteins into packages and distributes proteins produced by the cell • Found in both plants and animals vesicles • General name for little membrane-bound sacs that transport materials from place to place in the cell • Short-lived, they form and break-down as needed • Example: after a protein is made in the ribosome, part of the ER will pinch off and form a vesicle to transport the protein to the golgi apparatus. Mitochondria • Power House of the cell • Produces a usable form of Energy for the cell • Found in both plants and animals. Vacuole • Fluid filled sac used to temporarily store food, water, enzymes, and waste • Singular and large in plant cells, small and numerous in animal cells Lysosome • Contains digestive enzymes which help them to digest excess or worn-out cell parts, food and invading viruses and bacteria • More numerous in animal cells. Centrosome & Centriole • Found in animal cells and some algae • Small region of the cytoplasm that produces microtubules • Contains small structures called centrioles – – – – Occur in pairs Made of microtubules Help with Cell Division Organize microtubules to form cilia and flagella Flagellum & Cilia • Made of microtubules • Short numerous projections • Aid in cell locomotion and feeding (help to • Look like hairs move liquids past a • Function like oars in a cell) rowboat • Longer than cilia • Aid in cell locomotion • Move with whip-like and feeding (help to motion move liquids past a cell) • Usually only has 1-2 flagellum •Found in Some Animal Cells Flagellum & Cilia Cell Wall • Firm, protective, supportive structure that gives the cell its shape – Made of cellulose • Porous –there are channels that allow all molecules to enter through it. • Found in most bacteria, fungi, algae and plants Chloroplasts • In inner membrane there are disc-shaped sacs called thylakoids that contain chlorophyll – which is a green pigment that traps Energy from the Sun • Give plants their green color (only in plants!) • Produce food by capturing light energy and converting it into chemical energy.